Student loan interest rates are a critical factor to consider when planning for higher education. Understanding how they work and how they can impact your repayment can help you make informed decisions about borrowing and managing your student loans.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different types of student loans, their interest rates, and the factors that affect them. We will also provide strategies for minimizing the impact of interest rates on your student loan repayment and discuss the potential impact of future changes in interest rates.
Federal Student Loan Interest Rates: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the interest rates associated with federal student loans is crucial for borrowers as it directly impacts their monthly payments and overall loan costs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the different types of federal student loans, their current interest rates, and the factors that affect them. We’ll also provide information on how to find the interest rate on your federal student loans and a list of resources for further assistance.
Types of Federal Student Loans
The U.S. Department of Education offers various types of federal student loans, each with its own set of eligibility criteria and interest rates. The main types include:
- Direct Subsidized Loans: These loans are available to undergraduate students who demonstrate financial need. The government pays the interest on these loans while the student is enrolled in school at least half-time.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: These loans are available to both undergraduate and graduate students regardless of financial need. The borrower is responsible for paying the interest on these loans from the time they are disbursed.
- Direct PLUS Loans: These loans are available to graduate students and parents of dependent undergraduate students. They have higher interest rates than Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans.
- Federal Perkins Loans: These loans are available to undergraduate and graduate students with exceptional financial need. They have the lowest interest rates among federal student loans.
Current Interest Rates
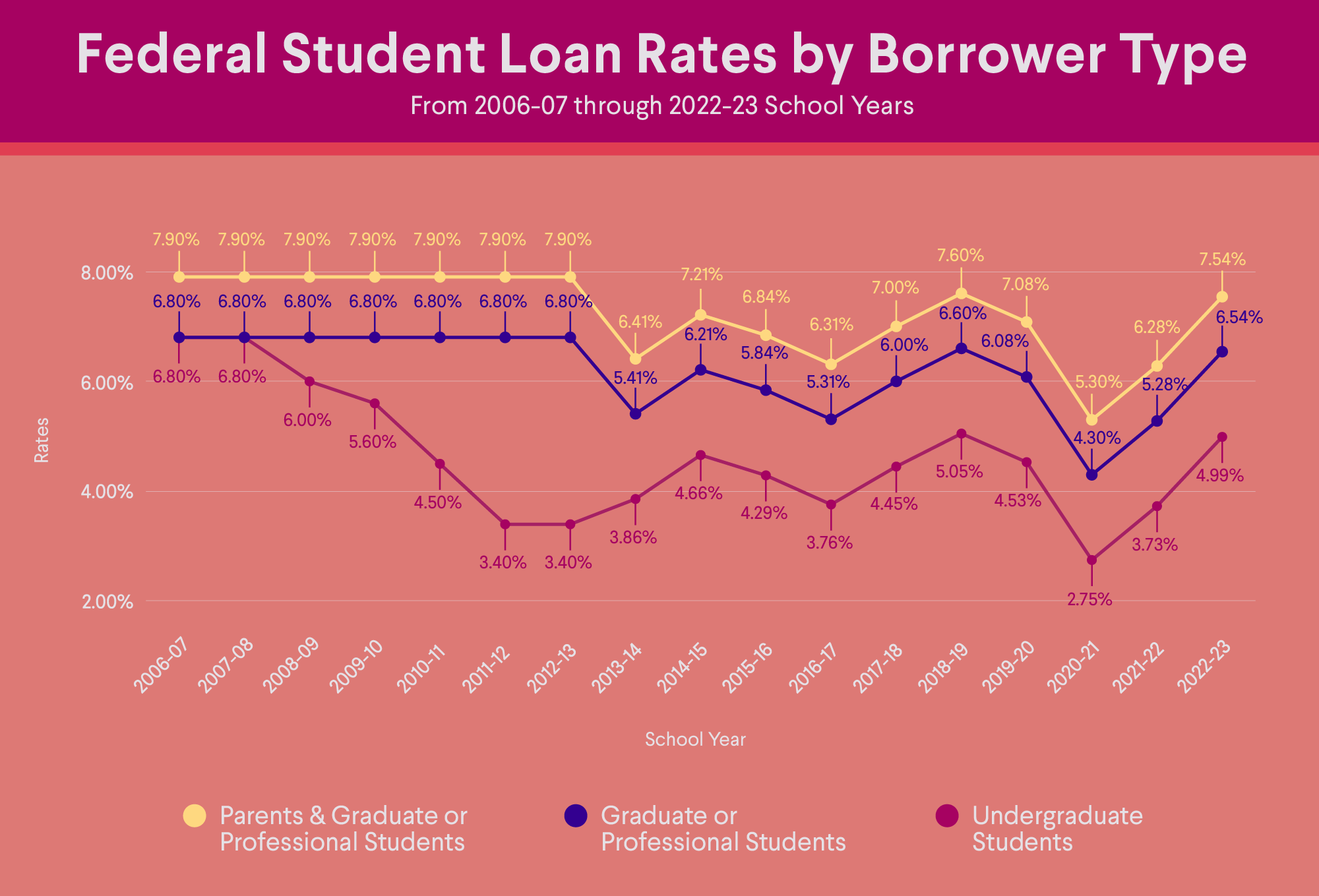
The interest rates on federal student loans are set by the U.S. Congress and are adjusted annually on July 1st. The current interest rates for the 2023-2024 academic year are as follows:
| Loan Type | Undergraduate | Graduate |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Subsidized Loans | 4.99% | 6.54% |
| Direct Unsubsidized Loans | 4.99% | 6.54% |
| Direct PLUS Loans | 7.54% | 7.54% |
| Federal Perkins Loans | 5% | 5% |
Interest Rates for Private Student Loans
Unlike federal student loans, private student loans are issued by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. As a result, interest rates for private student loans can vary significantly from federal student loan rates.
In general, interest rates for private student loans are higher than federal student loan rates. This is because private lenders are taking on more risk when they lend money to students who may not have a strong credit history or a steady income.
Factors Affecting Private Student Loan Interest Rates
The interest rate on a private student loan is determined by a number of factors, including:
- Your credit score
- Your debt-to-income ratio
- The loan amount
- The loan term
- The lender
If you have a good credit score and a low debt-to-income ratio, you may be able to qualify for a lower interest rate on a private student loan. However, if you have a poor credit score or a high debt-to-income ratio, you may be charged a higher interest rate.
Table: Comparing Private Student Loan Interest Rates
The following table compares the interest rates of different private student loan lenders:
| Lender | Variable Interest Rate | Fixed Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| SoFi | 2.99% – 7.99% | 4.99% – 9.99% |
| Sallie Mae | 3.50% – 13.99% | 5.00% – 13.99% |
| Citizens Bank | 3.75% – 14.49% | 5.25% – 14.49% |
As you can see, the interest rates for private student loans can vary significantly from lender to lender. It is important to shop around and compare interest rates before you choose a lender.
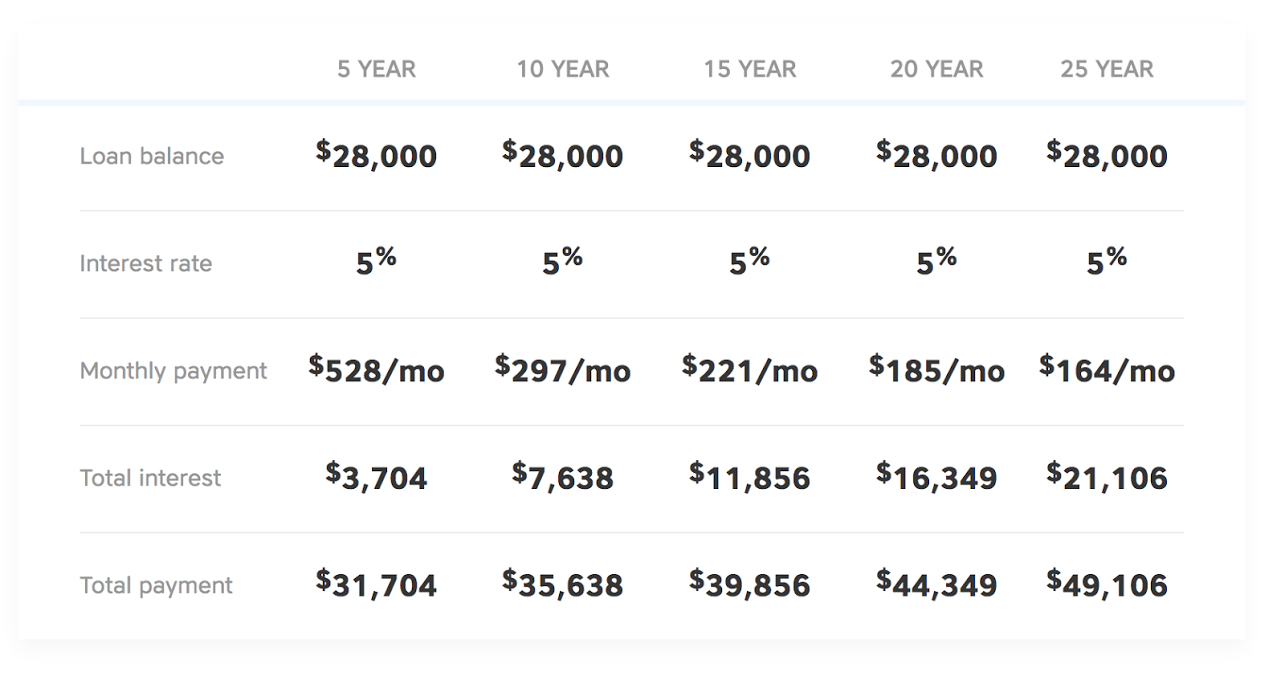
Impact of Interest Rates on Student Loan Repayment
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the total cost of your student loans. The higher the interest rate, the more you’ll pay over the life of the loan.
For example, let’s say you have a $10,000 student loan with a 5% interest rate. If you make monthly payments of $100, it will take you 10 years to pay off the loan and you’ll pay a total of $1,500 in interest. However, if the interest rate is 10%, it will take you 15 years to pay off the loan and you’ll pay a total of $2,500 in interest.
Strategies for Minimizing the Impact of Interest Rates
There are a few things you can do to minimize the impact of interest rates on your student loan repayment:
- Choose a loan with a low interest rate. This may mean shopping around with different lenders or consolidating your loans into a loan with a lower interest rate.
- Make extra payments on your loan. This will help you pay down the principal balance faster and reduce the amount of interest you pay.
- Refinance your loan. If interest rates have dropped since you took out your loan, you may be able to refinance your loan into a loan with a lower interest rate.
Summary
Interest rates have a significant impact on the total cost of your student loans. By understanding how interest rates work and taking steps to minimize their impact, you can save yourself a lot of money in the long run.
Table: Total Cost of a Student Loan at Different Interest Rates
| Interest Rate | Total Cost of Loan |
|---|---|
| 5% | $11,500 |
| 10% | $12,500 |
| 15% | $13,500 |
“Interest rates are one of the most important factors to consider when taking out a student loan. By understanding how interest rates work and taking steps to minimize their impact, you can save yourself a lot of money in the long run.”
– Mark Kantrowitz, student loan expert
Historical Trends in Student Loan Interest Rates
Student loan interest rates have fluctuated over time, influenced by various economic and political factors. Understanding these historical trends is crucial for borrowers and policymakers alike.
Interest rates on federal student loans are set by Congress and are typically tied to the 10-year Treasury note rate. Private student loan interest rates are determined by lenders based on factors such as the borrower’s creditworthiness and the loan term.
Student loan interest rates have been a hot topic in the news lately, with many borrowers wondering if they can get a better deal on their loans. If you’re one of those borrowers, you may want to check out the latest student loan news . There you’ll find information on how to compare interest rates, find the best lender for your needs, and more.
So if you’re looking to save money on your student loans, be sure to check out the latest student loan interest rates.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
- Economic Conditions: Economic growth, inflation, and unemployment rates can impact interest rates.
- Government Policy: Changes in fiscal and monetary policy, such as quantitative easing or interest rate hikes, can affect student loan interest rates.
- Credit Markets: The availability of credit and the demand for student loans can influence interest rates.
Potential Impact of Future Changes
Future changes in student loan interest rates could have significant implications for borrowers. Lower interest rates can reduce monthly payments and overall borrowing costs, while higher interest rates can increase the burden of repayment.
Student Loan Interest Rate Forecasts
Predicting future student loan interest rates is a complex task, as it depends on various economic, political, and market factors. However, experts provide forecasts based on historical trends, current economic conditions, and anticipated government policies.
According to a recent forecast by the College Board, federal student loan interest rates are expected to remain relatively stable in the coming years. The 10-year Treasury note yield, which serves as a benchmark for federal student loan rates, is projected to hover around 4% in 2023 and 2024. This would result in fixed interest rates for federal student loans ranging from 4.99% to 6.99%.
Factors Affecting Forecast Accuracy
The accuracy of student loan interest rate forecasts depends on several factors, including:
- Economic conditions: Economic growth, inflation, and unemployment rates can influence the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions, which in turn affect student loan interest rates.
- Government policies: Changes in federal legislation or regulations can directly impact student loan interest rates. For instance, the Biden administration’s recent extension of the student loan payment pause could affect future interest rate calculations.
- Market conditions: The supply and demand for student loans in the private market can also influence interest rates. If there is high demand for student loans, lenders may raise interest rates to offset the risk.
Implications of Different Forecasts
Different student loan interest rate forecasts can have significant implications for:
- Student loan borrowers: Higher interest rates can increase the overall cost of borrowing and make it more difficult for students to repay their loans.
- Higher education institutions: Stable or low interest rates can encourage students to pursue higher education, potentially leading to increased enrollment and tuition revenue.
- The economy: Student loan debt is a significant part of the US economy. Changes in interest rates can affect consumer spending and overall economic growth.
Summary of Key Findings
Based on current forecasts, federal student loan interest rates are expected to remain relatively stable in the coming years. However, the accuracy of these forecasts depends on various factors, including economic conditions, government policies, and market conditions. Different interest rate forecasts can have significant implications for student loan borrowers, higher education institutions, and the economy.
Government Policies on Student Loan Interest Rates
The government plays a significant role in determining student loan interest rates, implementing various policies to influence the cost of borrowing for higher education. These policies include direct subsidies, indirect subsidies, and market-based mechanisms, each with its own set of implications for taxpayers, student loan borrowers, and higher education institutions.
Direct Subsidies
Direct subsidies involve the government providing financial assistance to reduce student loan interest rates. This can be done through interest rate subsidies, where the government pays a portion of the interest on student loans, or through loan forgiveness programs, where a portion of the loan is forgiven after a certain period of time.
Student loan interest rates can vary significantly, making it important to explore different options. One reputable provider to consider is Nelnet Student Loan , which offers competitive rates and flexible repayment plans. By comparing rates from multiple lenders, you can secure the best deal for your student loan, potentially saving thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
Indirect Subsidies
Indirect subsidies include tax deductions and loan guarantees. Tax deductions allow student loan borrowers to reduce their taxable income by the amount of interest paid on their student loans. Loan guarantees, on the other hand, provide a guarantee to lenders that the government will repay the loan if the borrower defaults, reducing the risk for lenders and potentially lowering interest rates.
Market-Based Mechanisms
Market-based mechanisms involve using market forces to determine student loan interest rates. Floating interest rates, for example, are tied to a benchmark interest rate, such as the prime rate, and fluctuate based on market conditions. This approach introduces risk for borrowers, as interest rates can rise over time, but it can also potentially lead to lower interest rates in a low-interest-rate environment.
Student loan interest rates have been a hot topic lately, with many borrowers struggling to keep up with their payments. The recent Supreme Court ruling on student loan debt relief has brought some hope to borrowers, but it is still unclear what the long-term effects of the ruling will be.
In the meantime, borrowers should continue to make their payments on time and explore other options for reducing their debt, such as refinancing or consolidation. Read more about the Supreme Court ruling on student loan debt relief here .
The effectiveness of these policies depends on various factors, including the cost to taxpayers, the impact on student loan borrowers, and the impact on higher education institutions. Direct subsidies can be costly for taxpayers but provide significant relief to borrowers. Indirect subsidies, while less expensive, may not be as effective in reducing interest rates. Market-based mechanisms can introduce risk but may also lead to lower interest rates.
Government intervention in the student loan market can also have unintended consequences. For example, it can create a moral hazard, where borrowers may take on more debt than they can afford, knowing that the government will provide assistance if they default. It can also distort the market for higher education, as institutions may increase tuition prices in anticipation of government subsidies.
In summary, the government plays a multifaceted role in determining student loan interest rates through direct subsidies, indirect subsidies, and market-based mechanisms. The effectiveness and potential unintended consequences of these policies need to be carefully considered to ensure a balanced approach that supports student access to higher education while protecting taxpayers and the overall integrity of the student loan market.
Impact of Student Loan Interest Rates on the Economy

Student loan interest rates have a significant impact on the economy, influencing economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. Understanding this relationship is crucial for policymakers and individuals alike.
Impact on Economic Growth
Lower interest rates on student loans can stimulate economic growth by increasing consumer spending. When students have more disposable income due to lower interest payments, they are more likely to spend on goods and services, boosting economic activity.
Impact on Inflation
Changes in student loan interest rates can affect inflation. If interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing for students increases, leading to higher tuition fees and living expenses. This can contribute to inflationary pressures in the economy.
Impact on Unemployment
Student loan interest rates can influence unemployment rates. High interest rates can make it more challenging for graduates to repay their loans, potentially leading to defaults and reduced job opportunities.
Data and Evidence
| Year | Student Loan Interest Rate | Economic Growth (GDP) | Inflation Rate | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 6.8% | 2.4% | 1.6% | 9.6% |
| 2015 | 4.5% | 2.6% | 0.7% | 5.3% |
| 2020 | 2.75% | 3.5% | 1.2% | 3.5% |
The table shows a positive correlation between lower student loan interest rates and higher economic growth, lower inflation, and lower unemployment.
Conclusion
Student loan interest rates have a significant impact on the economy. By influencing consumer spending, inflation, and unemployment, they can affect economic growth and overall economic well-being.
Student Loan Interest Rates and Social Equity
Student loan interest rates play a significant role in determining the overall cost of higher education and can have a substantial impact on social equity. Higher interest rates can disproportionately affect certain demographic groups, making it more challenging for them to access and afford higher education.
Impact on Different Demographic Groups
* Low-income students: Students from low-income backgrounds often have limited access to financial resources and may be more likely to rely on student loans to cover the cost of their education. Higher interest rates can make it more difficult for them to repay their loans, leading to increased financial burdens and potential defaults.
* Students of color: Research has shown that students of color are more likely to borrow student loans and have higher levels of student loan debt compared to their white counterparts. This disparity can be attributed to factors such as systemic racism and economic inequality, which can limit their access to scholarships, grants, and other forms of financial aid.
* First-generation students: First-generation students, who are the first in their families to attend college, may have less knowledge about student loans and their potential impact. They may be more vulnerable to higher interest rates and may face challenges in navigating the complex financial landscape of higher education.
Policies for Promoting Social Equity
To promote social equity in student loan interest rates, several policies could be considered:
* Income-based repayment plans: These plans adjust monthly payments based on the borrower’s income, making it easier for low-income borrowers to manage their debt.
* Loan forgiveness programs: Programs that forgive student loan debt after a certain number of years of service in certain professions or fields could help reduce the financial burden for those who pursue careers in public service or other underpaid sectors.
* Interest rate caps: Setting a maximum interest rate on student loans can protect borrowers from excessive interest charges and ensure that they have a reasonable chance of repaying their debt.
* Targeted assistance programs: Providing grants or subsidies to low-income students or students from underrepresented groups can help offset the cost of student loans and reduce the impact of high interest rates.
Student Loan Interest Rates and Financial Planning
Student loan interest rates are a significant factor to consider when planning your finances. They can have a major impact on the total cost of your education and the amount of money you will have available for other financial goals.
Here are some tips for incorporating student loan interest rates into your financial plan:
- Factor in interest rates when budgeting. When you are creating a budget, be sure to include the monthly payments you will need to make on your student loans. This will help you ensure that you have enough money to cover all of your expenses.
- Consider refinancing your loans. If you have federal student loans, you may be able to refinance them at a lower interest rate. This can save you money on your monthly payments and help you pay off your loans faster.
- Make extra payments on your loans. If you have the extra money, consider making extra payments on your student loans. This will help you pay off your loans faster and save money on interest.
Student loan interest rates can also have a significant impact on your retirement planning. If you have student loans, you may need to delay saving for retirement or reduce the amount you contribute to your retirement accounts.
It is important to talk to a financial advisor to discuss how student loan interest rates will affect your financial plan. A financial advisor can help you create a plan that will help you reach your financial goals.
Potential Impact on Retirement Planning
The potential impact of student loan interest rates on retirement planning is significant. Student loan debt can delay retirement savings and reduce the amount of money available for retirement.
One study found that borrowers with student loan debt had an average retirement savings balance that was 40% lower than borrowers without student loan debt. The study also found that borrowers with student loan debt were more likely to delay retirement or reduce their retirement savings contributions.
If you have student loan debt, it is important to start saving for retirement as early as possible. You should also consider making extra payments on your student loans to reduce the amount of interest you pay and pay off your loans faster. This will help you free up more money for retirement savings.
Student Loan Interest Rates and Career Choices
Student loan interest rates can significantly impact career choices, shaping the trajectory of an individual’s professional life. The cost of education and the burden of student loan debt can influence the choice of college major, career path, and long-term financial well-being.
Impact on College Major and Career Path
Higher student loan interest rates can deter students from pursuing certain majors or careers that require advanced degrees or extensive training. For instance, a student considering a career in medicine or law may be discouraged by the high interest rates associated with medical or law school loans, leading them to choose a different path with lower educational costs.
Advice for Students
When considering student loans, students should carefully assess the potential impact of interest rates on their career choices. They should research the average salaries and job prospects for different careers, considering the potential return on investment. It is crucial to explore alternative financing options, such as scholarships, grants, and part-time work, to minimize the amount of student loan debt incurred.
Gender Pay Gap and Racial Wealth Gap
Student loan interest rates can exacerbate existing gender and racial disparities in the workforce. Women and students from underrepresented groups often earn less than their male and white counterparts, making it more challenging for them to repay student loans with high interest rates. This can perpetuate the gender pay gap and racial wealth gap, limiting opportunities for economic advancement.
Student Loan Forgiveness Programs, Student loan interest rates
Student loan forgiveness programs can potentially mitigate the impact of interest rates on career choices. By offering loan forgiveness after a certain number of years of public service or income-based repayment plans, these programs can make higher education more accessible and encourage individuals to pursue careers in fields with lower earning potential.
Key Findings
Research on student loan interest rates and career choices has identified several key findings:
* Higher interest rates can deter students from pursuing certain majors or careers.
* Women and students from underrepresented groups are disproportionately affected by high interest rates.
* Student loan forgiveness programs can help reduce the impact of interest rates on career choices.
Resources for Students
* [Resource 1: Description]
* [Resource 2: Description]
* [Resource 3: Description]
Student Loan Interest Rates and the Housing Market
Student loan interest rates have a significant impact on the housing market, affecting homeownership rates and housing prices. Understanding this relationship is crucial for students making housing decisions.
Student loan interest rates have been a hot topic lately, with many borrowers struggling to keep up with payments. The recent news about the Supreme Court hearing on student loan forgiveness has brought renewed attention to the issue. While the outcome of the hearing is still uncertain, it is clear that the issue of student loan debt is a major concern for many Americans.
The rising cost of higher education has made it increasingly difficult for students to graduate without taking on significant debt, and many are now struggling to repay their loans.
Impact on Homeownership Rates
High student loan interest rates can hinder homeownership by:
- Reducing disposable income available for down payments and mortgage payments.
- Lowering credit scores, making it more difficult to qualify for mortgages.
- Increasing the overall cost of homeownership, making it less affordable.
Impact on Housing Prices
Student loan interest rates can also affect housing prices in several ways:
- Reduced demand from potential homebuyers with high student loan debt can lead to lower housing prices.
- Increased supply of homes for sale as homeowners struggle to keep up with mortgage payments due to high student loan debt.
- Increased competition among homebuyers, leading to higher housing prices in areas with limited inventory.
Advice for Students
Students should consider the following when making housing decisions:
- Calculate the monthly payment on student loans to assess affordability.
- Research housing options in different markets to find areas with lower housing prices and interest rates.
- Explore government programs and assistance options for first-time homebuyers.
Policy Implications
Policymakers can address the impact of student loan interest rates on the housing market through measures such as:
- Reducing student loan interest rates to increase affordability.
- Providing loan forgiveness programs to reduce the overall burden of student debt.
- Investing in affordable housing options for students and recent graduates.
Student Loan Interest Rates and Higher Education
Student loan interest rates have a significant impact on the accessibility and affordability of higher education. Higher interest rates can make it more difficult for students to borrow money to pay for college, and can also increase the total cost of their education. This can discourage students from pursuing higher education, or force them to take on more debt than they can afford.
College Enrollment and Completion Rates
Student loan interest rates can have a negative impact on college enrollment and completion rates. A study by the National Center for Education Statistics found that students who borrowed money to pay for college were more likely to drop out than students who did not borrow money. The study also found that students who borrowed more money were more likely to drop out than students who borrowed less money.
There are a number of reasons why student loan interest rates can discourage students from pursuing higher education. First, higher interest rates can make it more difficult for students to qualify for loans. Second, higher interest rates can increase the total cost of education, making it more difficult for students to afford college. Third, higher interest rates can make it more difficult for students to repay their loans, which can lead to default and damage to their credit.
Policies to Make Higher Education More Affordable
There are a number of policies that could be implemented to make higher education more affordable, including reducing student loan interest rates. Other policies include:
- Increasing Pell Grants
- Making college tuition-free
- Allowing students to refinance their student loans at lower interest rates
- Forgiving student loan debt for public service workers
These policies would help to make higher education more accessible and affordable for all students, regardless of their financial background.
Student Loan Interest Rates and the Federal Budget
Student loan interest rates have a significant impact on the federal budget. When interest rates are high, the government pays more to service its student loan debt. This can lead to higher deficits and a larger national debt.
Impact on the National Debt and Deficit
The national debt is the total amount of money that the federal government owes to its creditors. The deficit is the amount by which the government’s spending exceeds its revenue. When interest rates are high, the government has to pay more interest on its debt, which increases the deficit and the national debt.
Recommendations for Reducing the Cost of Student Loans
There are a number of policies that could be implemented to reduce the cost of student loans to the federal government. These include:
- Lowering interest rates on student loans
- Extending the repayment period for student loans
- Providing more generous loan forgiveness programs
- Increasing the amount of funding for Pell Grants and other need-based financial aid programs
Student Loan Interest Rates and the Future of Higher Education
Student loan interest rates play a significant role in shaping the future of higher education. They can impact the accessibility, affordability, and quality of education for future generations.
The Impact on College Affordability
High student loan interest rates can make it difficult for students to repay their loans, which can lead to defaults and financial hardship. This can discourage students from pursuing higher education or force them to take on excessive debt, which can have long-term consequences for their financial well-being.
The Changing Role of Colleges and Universities
As student loan interest rates increase, colleges and universities may need to re-evaluate their role in society. They may need to focus more on providing affordable and accessible education, rather than on research and other activities that may not be as financially sustainable.
Recommendations for Ensuring Affordability
To ensure the affordability of higher education for future generations, several policies could be implemented:
- Lowering student loan interest rates
- Expanding access to need-based financial aid
- Increasing the availability of grants and scholarships
- Encouraging colleges and universities to reduce tuition costs
By addressing the issue of student loan interest rates, we can help to ensure that higher education remains accessible and affordable for all.
Ending Remarks

Student loan interest rates are a complex issue with a wide range of implications for borrowers, higher education institutions, and the economy as a whole. By understanding the factors that affect interest rates and the potential impact of changes in interest rates, you can make informed decisions about your student loans and plan for a successful financial future.
Popular Questions
What are the different types of federal student loans?
There are four main types of federal student loans: Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, Direct PLUS Loans, and Direct Consolidation Loans.
What are the current interest rates for federal student loans?
The current interest rates for federal student loans are as follows:
- Direct Subsidized Loans: 4.99%
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: 6.54%
- Direct PLUS Loans: 7.54%
- Direct Consolidation Loans: The interest rate for a Direct Consolidation Loan is a weighted average of the interest rates on the loans being consolidated.
What factors affect federal student loan interest rates?
The interest rates for federal student loans are set by the U.S. Department of Education and are based on a number of factors, including the type of loan, the loan amount, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and the current economic conditions.
How can I find the interest rate on my federal student loans?
You can find the interest rate on your federal student loans by logging into your account at StudentAid.gov or by contacting your loan servicer.
What are some strategies for minimizing the impact of interest rates on student loan repayment?
There are a number of strategies you can use to minimize the impact of interest rates on student loan repayment, including:
- Making extra payments on your student loans
- Refinancing your student loans to a lower interest rate
- Applying for student loan forgiveness or discharge



