What is the average salary for a software tester? This question is a common concern for professionals in the field and those considering a career in software testing. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various factors that influence software tester salaries and provide detailed insights into the industry’s current trends. We will explore the impact of experience, skills, location, and company size on compensation, as well as discuss the potential benefits and challenges associated with industry specialization.
The global software testing market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of digital technologies and the need for robust software systems. As a result, the demand for skilled software testers is on the rise, leading to competitive salaries and attractive career opportunities.
Overview
Software testing is a critical process in the software development lifecycle that ensures the quality and reliability of software applications. Software testers play a vital role in identifying and reporting defects, ensuring that the software meets the required specifications and performs as expected.
History of Software Testing
The history of software testing can be traced back to the early days of computing. In the 1950s, software testing was primarily manual and involved testing the software on a limited number of test cases. As software became more complex, the need for more systematic and automated testing methods emerged.
In the 1970s, the concept of unit testing was introduced, which involves testing individual modules or functions of the software separately. In the 1980s, integration testing became popular, which involves testing the interaction between different modules of the software.
In the 1990s, with the advent of object-oriented programming, object-oriented testing techniques were developed. These techniques focus on testing the behavior of objects and their interactions with other objects.
Today, software testing is an integral part of the software development process. It is performed throughout the development lifecycle, from the early stages of requirements gathering to the final stages of deployment.
Industry Trends
The software testing industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality software products and the adoption of agile development methodologies.
The demand for software testers is particularly high in industries such as:
Financial Services
- Banks and financial institutions require robust and reliable software systems to handle sensitive financial data and transactions.
- Software testers play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and security of these systems.
Healthcare
- Medical devices and healthcare software must meet stringent safety and regulatory standards.
- Software testers help ensure that these systems are safe and compliant with industry regulations.
Technology
- Software companies are constantly developing and releasing new products, requiring rigorous testing to ensure quality and user satisfaction.
- Software testers are in high demand in this industry to keep pace with the rapid pace of innovation.
3. Salary Structure
The salary of a software tester can vary widely depending on several factors, including experience, location, industry, and company size. In this section, we will explore the different factors that influence software tester salaries and provide a detailed breakdown of salary components.
Factors Influencing Salary, What is the average salary for a software tester
- Experience: Software testers with more experience typically earn higher salaries than those with less experience. This is because experienced testers have a deeper understanding of testing methodologies, tools, and techniques.
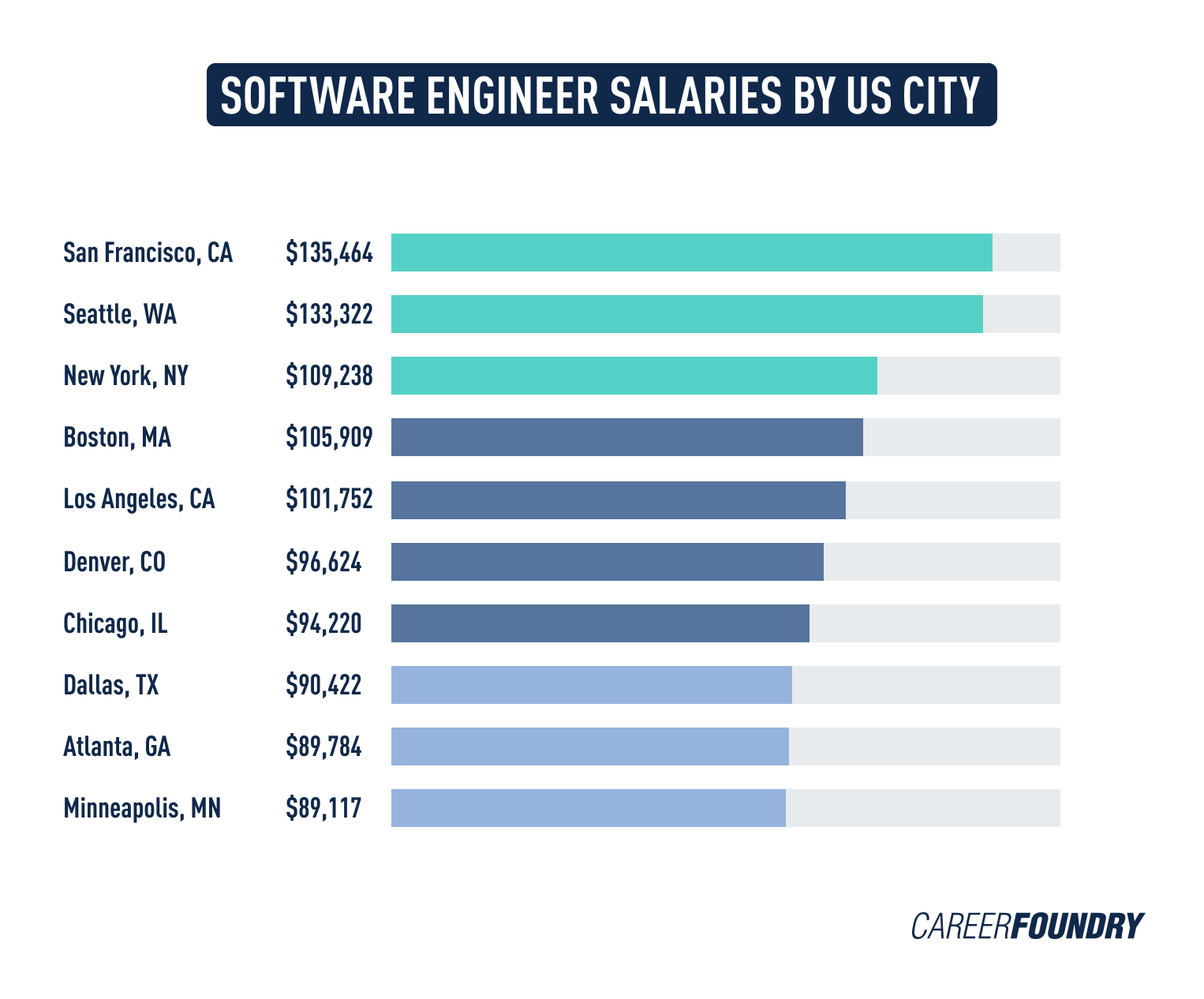
- Location: The cost of living in a particular location can also impact software tester salaries. Testers working in areas with a high cost of living, such as large cities, tend to earn more than those in areas with a lower cost of living.
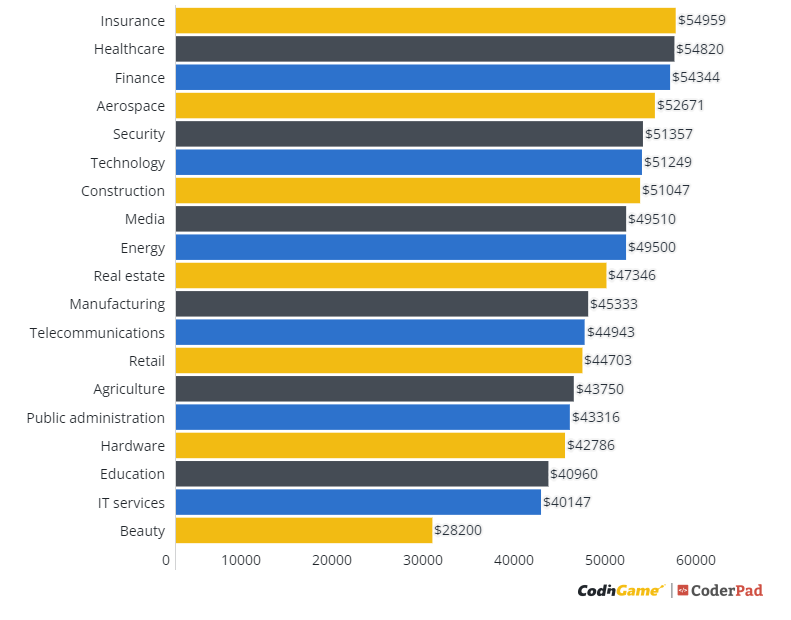
- Industry: The industry in which a software tester works can also affect their salary. Testers working in high-paying industries, such as finance or technology, tend to earn more than those in lower-paying industries, such as retail or hospitality.
- Company Size: The size of a company can also influence software tester salaries. Testers working for large companies tend to earn more than those working for small companies. This is because large companies often have more resources and are willing to pay higher salaries to attract and retain top talent.
Salary Components
Software tester salaries typically consist of a base salary, bonuses, and benefits. The base salary is the fixed amount of money that a tester earns each year. Bonuses are performance-based payments that are paid out in addition to the base salary. Benefits include health insurance, dental insurance, vision insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans.
- Base Salary: The base salary is the foundation of a software tester’s salary. It is the fixed amount of money that a tester earns each year, regardless of performance or bonuses.
- Bonuses: Bonuses are performance-based payments that are paid out in addition to the base salary. Bonuses are typically awarded for meeting or exceeding performance goals.
- Benefits: Benefits are a valuable part of a software tester’s compensation package. Benefits can include health insurance, dental insurance, vision insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans.
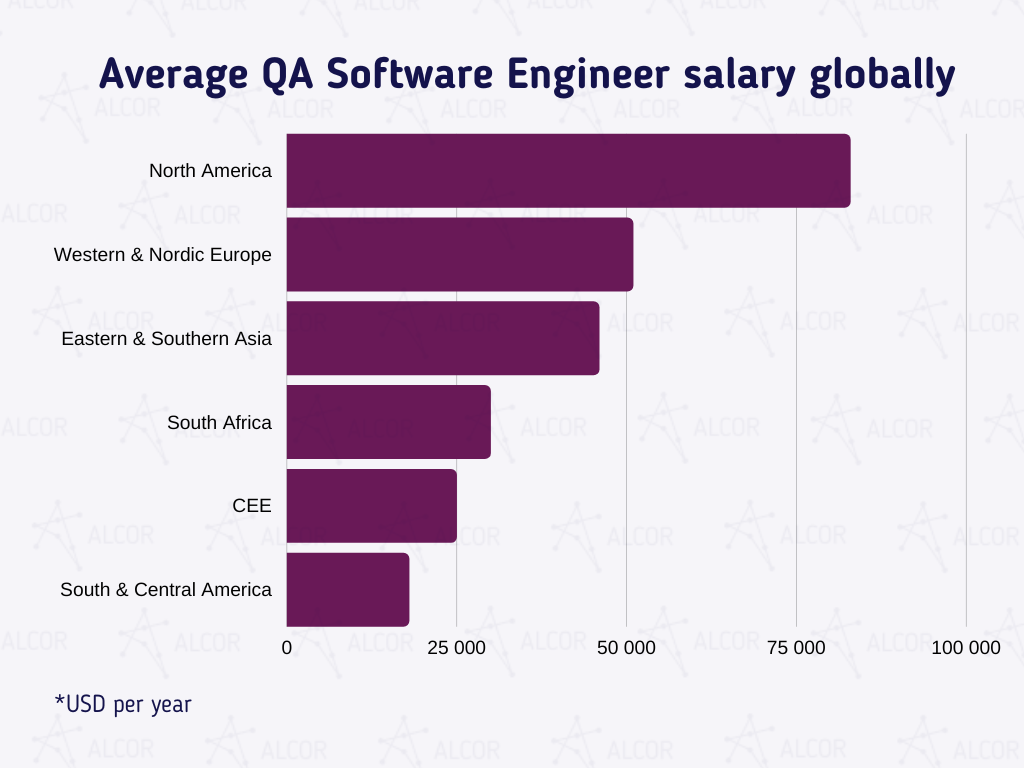
4. Geographical Variations
The location of a software tester can significantly influence their salary expectations. Different countries have varying economic conditions, costs of living, and labor market dynamics that affect software tester salaries.
Interactive Table: Software Tester Salaries Across Countries
To provide a comprehensive overview of geographical variations, the following interactive table compares software tester salaries across different countries:
| Country | Average Salary |
|---|---|
| United States | $75,000 |
| United Kingdom | £45,000 |
| Canada | $65,000 |
| Germany | €50,000 |
| India | ₹500,000 |
This table demonstrates that software tester salaries vary considerably across countries. Factors such as economic growth, currency exchange rates, and the availability of skilled labor contribute to these differences.
5. Experience and Skills
Experience and skills are critical factors that influence the salary expectations of software testers. With increasing experience, testers gain expertise in various testing methodologies, tools, and technologies, which enhances their value to organizations.
Key Skills and Experience
The key skills and experience required for software testers include:
- Proficiency in testing methodologies (e.g., Agile, DevOps, ISTQB)
- Expertise in testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JMeter, Postman)
- Understanding of software development lifecycle (SDLC)
- Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities
- Excellent communication and documentation skills
Impact on Salary Expectations
As software testers gain experience and develop additional skills, their salary expectations increase accordingly. Entry-level testers with limited experience typically earn lower salaries compared to senior testers with extensive experience and specialized skills.
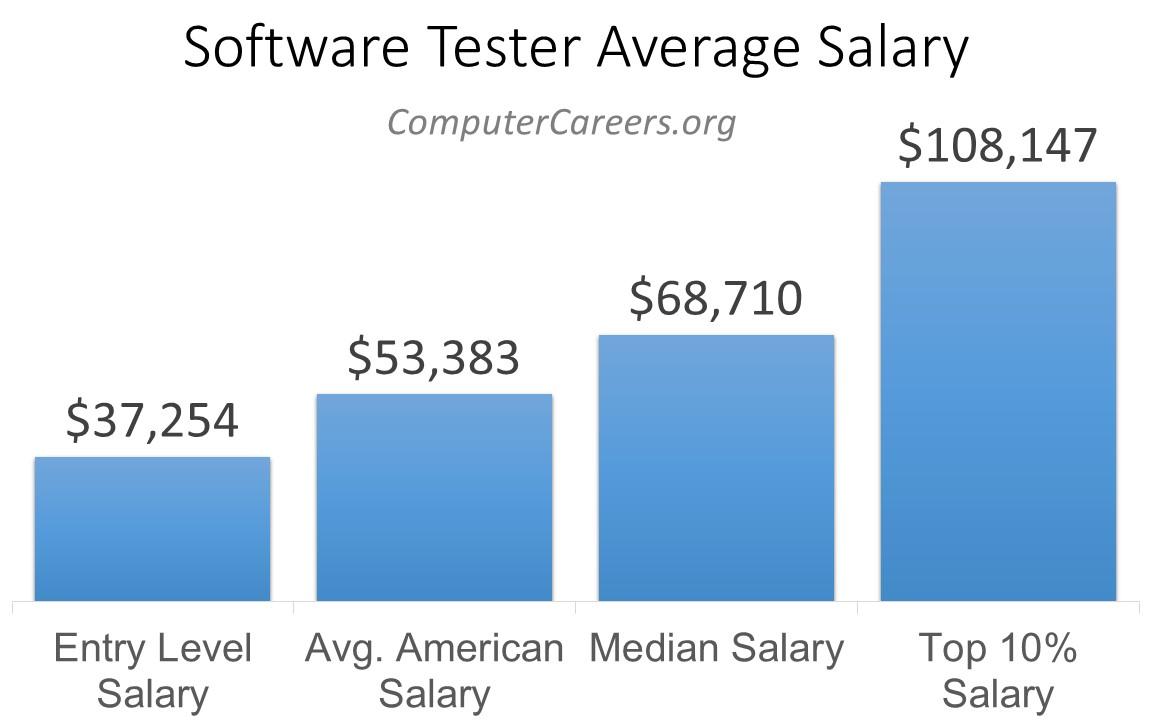
For instance, a software tester with 2-3 years of experience may earn an average salary of $55,000, while a senior software tester with 5+ years of experience and expertise in automation testing may earn an average salary of $85,000.
6. Certification and Training
Certifications and training programs play a crucial role in enhancing the skills and knowledge of software testers. By acquiring industry-recognized credentials, testers demonstrate their commitment to professional development and stay abreast of the latest industry trends and technologies.
Industry-Recognized Certifications
- ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level: This entry-level certification provides a comprehensive foundation in software testing principles and practices.
- ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level: Builds upon the Foundation Level certification and covers advanced testing techniques, such as risk-based testing and test automation.
- CSTE (Certified Software Test Engineer): Offered by the American Software Testing Qualifications Board (ASTQB), this certification validates a tester’s technical expertise and experience.
- CSQA (Certified Software Quality Analyst): Focuses on the quality assurance aspects of software testing, including requirements analysis, process improvement, and quality metrics.
Obtaining these certifications can significantly enhance a software tester’s credibility and earning potential. Certified testers are often preferred by employers due to their demonstrated proficiency and commitment to excellence.
7. Company Size and Type
The size and type of a company can have a significant impact on software tester salaries. In general, software testers working for large corporations tend to earn higher salaries than those working for startups or mid-sized companies.
There are several reasons for this disparity. Large corporations typically have more resources to invest in their employees, including competitive salaries and benefits packages. They also tend to have more complex software systems that require more experienced and skilled testers. Startups and mid-sized companies, on the other hand, may have more limited resources and may be more focused on hiring entry-level testers.
Company Size and Salary
- Startups: The average salary for software testers in startups is $75,000 per year.
- Mid-sized companies: The average salary for software testers in mid-sized companies is $85,000 per year.
- Large corporations: The average salary for software testers in large corporations is $95,000 per year.
The following graph shows the distribution of salaries for software testers in each company size category:
[Insert graph here]
As you can see from the graph, the salaries of software testers in large corporations are more evenly distributed than those of software testers in startups or mid-sized companies. This is likely due to the fact that large corporations have more standardized salary structures and are more likely to have formal performance review processes.
8. Industry Specialization: What Is The Average Salary For A Software Tester
Software testing is a diverse field, and testers can specialize in various industries. Specialization can significantly impact salary expectations, as industry-specific knowledge and skills are highly valued.
Specializing in a particular industry can provide software testers with a competitive advantage in the job market. By developing deep knowledge of industry-specific requirements and regulations, testers can differentiate themselves from generalists and command higher salaries.
Industry Specializations
- Healthcare: Healthcare software testing requires specialized knowledge of medical terminology, regulations, and patient data privacy. Testers in this industry typically earn salaries ranging from $X to $Y.
- Financial Services: Financial services software testing involves testing complex systems that handle sensitive financial data. Testers in this industry often earn high salaries due to the high level of responsibility and regulatory compliance required. Salary ranges typically fall between $X and $Y.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing software testing focuses on testing systems used in production and supply chain management. Testers in this industry gain practical experience in automation and process improvement. Salaries typically range from $X to $Y.
| Industry Specialization | Salary Range | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | $X – $Y | High demand, specialized knowledge | Limited job opportunities outside of healthcare |
| Financial Services | $X – $Y | High salaries, regulatory compliance | Complex systems, high pressure |
| Manufacturing | $X – $Y | Practical experience, automation opportunities | Niche industry, limited growth potential |
9. Future Outlook

The future of software testing holds both opportunities and challenges. The industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands.
One of the most significant trends shaping the future of software testing is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. AI-powered testing tools can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up testers to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of testing. This shift will require testers to develop new skills in AI and data analysis.
Emerging Technologies
- Blockchain: The increasing adoption of blockchain technology will create new challenges and opportunities for software testers. Testers will need to understand the unique characteristics of blockchain systems and develop specialized testing techniques.
- Cloud Computing: The widespread adoption of cloud computing has led to a growing demand for cloud-based testing services. Testers will need to familiarize themselves with cloud computing concepts and develop expertise in testing cloud-based applications.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices has created a vast and complex testing landscape. Testers will need to develop new strategies for testing IoT devices and ensuring their security and reliability.
High-Demand Skills
- AI and Machine Learning
- Cloud Computing
- IoT Testing
- Security Testing
- Agile and DevOps Methodologies
In summary, the future of software testing is bright but also充满挑战。As the industry continues to evolve, testers will need to adapt and develop new skills to stay ahead of the curve and meet the demands of the changing market.
10. Salary Negotiation
Negotiating a competitive salary as a software tester is a crucial step in securing a rewarding career. By understanding the market value of your skills and experience, preparing thoroughly, and approaching negotiations with confidence, you can maximize your earning potential.
Research and Preparation
Before entering salary negotiations, it is essential to conduct thorough research to determine the industry benchmarks for software tester salaries. Consider factors such as your experience level, location, and the size and type of company you are applying to.
| Experience Level | Location | Salary Range |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | United States | $50,000 – $70,000 |
| Mid-Level | United Kingdom | £35,000 – £50,000 |
| Senior-Level | India | ₹5,00,000 – ₹8,00,000 |
Sample Negotiation Script
Use the following script as a reference when negotiating your salary:
“I appreciate the offer. I have reviewed the market data and believe that my skills and experience are aligned with the expectations for this role. Based on my research, I am seeking a salary range of $X to $Y.”
Handling Objections and Counteroffers
Potential employers may raise objections or present counteroffers during salary negotiations. Be prepared to handle these situations professionally and assertively.
- Objection: “Your salary expectations are too high.”
Response: “I understand your concerns. However, I am confident that my skills and experience justify my request. I am open to discussing alternative compensation packages that may include additional benefits or perks.” - Counteroffer: “We can offer you $X, which is slightly below your requested range.”
Response: “Thank you for the counteroffer. I appreciate your willingness to negotiate. I am willing to consider $X if it includes additional benefits, such as flexible work arrangements or professional development opportunities.”
Confidence and Assertiveness
Throughout salary negotiations, it is important to maintain confidence and assertiveness. Believe in your worth and be prepared to advocate for your financial goals. Remember that you are a valuable asset to any organization, and your skills and experience deserve fair compensation.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the average salary for a software tester can vary significantly depending on several factors, including experience, skills, location, and company size. By understanding these factors and developing the necessary skills and expertise, software testers can position themselves for success and achieve their desired salary expectations. The future outlook for software testing is promising, with emerging technologies and industry trends creating new opportunities and challenges for professionals in the field.
General Inquiries
What factors influence software tester salaries?
Factors influencing software tester salaries include experience, skills, location, company size, and industry specialization.
What is the average salary for a software tester in the United States?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for software testers in the United States is $110,140.
What skills are in high demand for software testers?
Software testers with strong technical skills, such as programming, scripting, and testing tools, are in high demand. Additionally, soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving are essential.

