In the realm of personal finance, the Save Student Loan Plan has emerged as a beacon of hope for countless individuals burdened by the weight of student loan debt. This groundbreaking initiative promises to revolutionize the way we approach higher education financing, offering a lifeline to those struggling to repay their loans.
With the potential to transform the lives of millions of Americans, the Save Student Loan Plan has sparked a nationwide conversation. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of the plan, exploring its eligibility criteria, potential benefits, and the challenges that lie ahead.
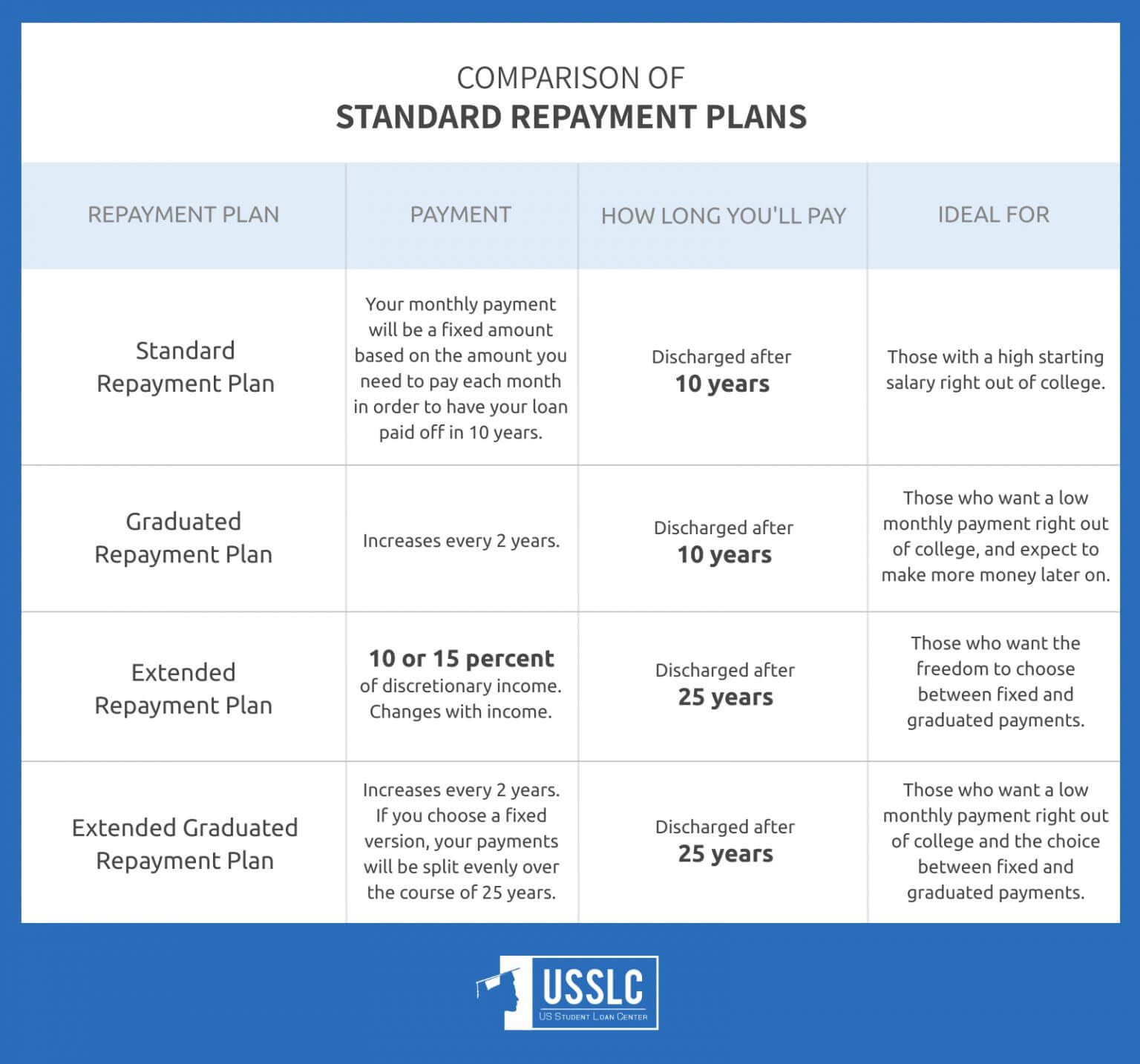
Overview of Student Loan Forgiveness Plan

The recently announced student loan forgiveness plan aims to provide relief to millions of borrowers struggling with student loan debt. The plan has several key provisions, including:
Eligibility Criteria:
- Borrowers who have received Pell Grants are eligible for up to $20,000 in forgiveness.
- Borrowers who have not received Pell Grants are eligible for up to $10,000 in forgiveness.
- The income threshold for eligibility is $125,000 for individuals and $250,000 for married couples filing jointly.
Application Process:
Borrowers can apply for forgiveness through a simple online application that will be available in early October. The application will require borrowers to provide their name, Social Security number, and other basic information.
Benefits of Student Loan Forgiveness
Student loan forgiveness holds immense potential to transform the lives of individuals and revitalize the economy. By alleviating the crushing burden of student debt, it can unleash a wave of financial freedom, economic growth, and social equity.
Reduced Financial Burden and Increased Disposable Income
Student loan forgiveness would significantly reduce the financial burden faced by millions of Americans. With the average student loan debt exceeding $30,000, many borrowers struggle to make ends meet, save for the future, or purchase a home. Forgiveness would free up a substantial portion of their monthly income, allowing them to invest in themselves, their families, and the economy.
Boosted Economic Growth
The increased disposable income resulting from student loan forgiveness would have a ripple effect on the economy. Consumers would spend more on goods and services, boosting demand and stimulating job creation. Studies have shown that for every dollar of student debt forgiven, $1.20 is added to the GDP.
Enhanced Economic Mobility
Student loan forgiveness would particularly benefit low-income borrowers, first-generation college students, and minority borrowers who disproportionately face higher levels of student debt. By reducing the financial barriers they face, forgiveness would promote economic mobility and create a more level playing field.
Potential Economic Benefits
Quantifying the potential economic benefits of student loan forgiveness is challenging, but estimates suggest it could increase consumer spending by billions of dollars and create millions of new jobs. The Congressional Budget Office has estimated that forgiving $10,000 of student debt for all borrowers would cost $377 billion but would also increase GDP by $86 billion over the next decade.
Funding Mechanisms
Various funding mechanisms have been proposed for student loan forgiveness, including reallocating funds from other government programs, increasing taxes on high-income earners, or creating a new revenue stream. The specific funding mechanism chosen would depend on the scope and design of the forgiveness program.
While many have benefited from the save student loan plan, it’s essential to stay updated on the latest student loan news . These updates can inform you about potential changes to the plan or new programs that could provide additional assistance.
By staying informed, you can ensure you’re taking advantage of all the benefits available to you under the save student loan plan.
Counterarguments and Concerns
While student loan forgiveness offers significant potential benefits, it also raises some concerns, including:
- Fairness: Some argue that it is unfair to forgive student loans for some borrowers but not others, or that it rewards those who made poor financial decisions.
- Moral hazard: Others worry that student loan forgiveness could encourage future students to take on more debt, knowing that it may be forgiven in the future.
These concerns should be carefully considered and addressed in any student loan forgiveness program. However, the potential benefits of forgiveness outweigh these concerns and make it a worthwhile investment in the future of our economy and our society.
Challenges and Limitations of Student Loan Forgiveness
The student loan forgiveness plan has been met with mixed reactions. While many borrowers welcome the relief, others have raised concerns about its fairness, cost, and potential impact on the higher education system.
One of the biggest challenges of student loan forgiveness is determining who is eligible. The Biden administration has proposed forgiving up to $10,000 in federal student loan debt for borrowers who earn less than $125,000 per year, or $250,000 for married couples. However, this income threshold may not be high enough to capture all borrowers who are struggling to repay their loans.
The recent save student loan plan is a much-needed relief for millions of borrowers struggling to repay their student debt. With the student loan pause now extended until the end of the year, borrowers have more time to get their finances in order and plan for the future.
This extension provides much-needed flexibility and allows borrowers to focus on other financial priorities, such as saving for a down payment on a house or investing for retirement. The save student loan plan is a positive step towards helping borrowers manage their student debt and achieve their financial goals.
Another challenge is the cost of student loan forgiveness. The Biden administration has estimated that the plan will cost $300 billion over the next decade. This is a significant amount of money, and it is unclear how the government will pay for it. Some critics have argued that the cost of student loan forgiveness should be borne by the borrowers themselves, rather than by taxpayers.
Finally, there are concerns about the potential impact of student loan forgiveness on the higher education system. Some critics have argued that student loan forgiveness will encourage colleges and universities to raise tuition prices, knowing that the government will be there to bail out students who cannot afford to repay their loans. Others have argued that student loan forgiveness will make it more difficult for students from low-income families to attend college, as they will be less likely to qualify for financial aid.
Fairness
One of the biggest concerns about student loan forgiveness is that it is not fair. Critics argue that it is unfair to forgive the debts of borrowers who have already graduated from college, while leaving behind those who are still struggling to repay their loans.
Additionally, critics argue that student loan forgiveness is unfair to taxpayers who have already paid off their own student loans, or who never went to college.
Cost
Another concern about student loan forgiveness is its cost. The Biden administration has estimated that the plan will cost $300 billion over the next decade. This is a significant amount of money, and it is unclear how the government will pay for it.
Some critics have argued that the cost of student loan forgiveness should be borne by the borrowers themselves, rather than by taxpayers.
Impact on the Higher Education System
Finally, there are concerns about the potential impact of student loan forgiveness on the higher education system. Some critics have argued that student loan forgiveness will encourage colleges and universities to raise tuition prices, knowing that the government will be there to bail out students who cannot afford to repay their loans.
Others have argued that student loan forgiveness will make it more difficult for students from low-income families to attend college, as they will be less likely to qualify for financial aid.
– Analyze the potential economic impact of student loan forgiveness on various sectors, such as education, housing, and healthcare.
The forgiveness of student loans could have a significant impact on various sectors of the economy. In the education sector, it could lead to increased enrollment and completion rates, as well as a reduction in the cost of higher education. In the housing sector, it could lead to increased homeownership rates, as well as a reduction in the cost of housing. In the healthcare sector, it could lead to increased access to healthcare services, as well as a reduction in the cost of healthcare.
Education
- Increased enrollment and completion rates: Student loan forgiveness could make it more affordable for students to attend college, which could lead to increased enrollment and completion rates.
- Reduced cost of higher education: Student loan forgiveness could reduce the cost of higher education for students, which could make it more affordable for them to attend college.
Housing
- Increased homeownership rates: Student loan forgiveness could make it more affordable for people to buy homes, which could lead to increased homeownership rates.
- Reduced cost of housing: Student loan forgiveness could reduce the cost of housing for people, which could make it more affordable for them to buy homes.
Healthcare
- Increased access to healthcare services: Student loan forgiveness could make it more affordable for people to access healthcare services, which could lead to increased access to healthcare services.
- Reduced cost of healthcare: Student loan forgiveness could reduce the cost of healthcare for people, which could make it more affordable for them to access healthcare services.
Political Implications of Student Loan Forgiveness: Save Student Loan Plan
The student loan forgiveness plan has significant political implications that will impact public opinion, voter turnout, and the political landscape. It has the potential to reshape the relationship between the government and citizens, as well as influence the future of higher education policy.
Impact on Public Opinion
The student loan forgiveness plan is likely to have a positive impact on public opinion. Many Americans are struggling with student loan debt, and the prospect of having a portion of that debt forgiven could be seen as a major relief. This could lead to increased support for the government and the political party that enacted the plan.
Impact on Voter Turnout
The student loan forgiveness plan could also have a significant impact on voter turnout. Young people, who are more likely to have student loan debt, are often less likely to vote. However, the prospect of having their student loan debt forgiven could motivate them to turn out in greater numbers. This could have a significant impact on the outcome of elections.
As part of the Biden administration’s efforts to save the student loan plan, the government has introduced a student loan forgiveness application for borrowers who meet certain criteria. This move aims to provide relief to millions of Americans struggling with student debt and support the overall economy.
The save student loan plan continues to be a crucial aspect of the administration’s efforts to address the financial challenges faced by students and their families.
Impact on the Political Landscape
The student loan forgiveness plan could also reshape the political landscape. It could lead to a realignment of political coalitions, as voters who have benefited from the plan become more supportive of the government and the political party that enacted it. It could also lead to a shift in the focus of political debate, as issues related to higher education and economic inequality become more prominent.
Alternative Solutions to Student Loan Debt
Student loan debt has become a major issue for millions of Americans, with the total amount owed now exceeding $1.7 trillion. This has led to a growing demand for alternative solutions to address this problem.
Income-driven repayment plans are one option that can help borrowers manage their student loan debt. These plans allow borrowers to make payments based on their income and family size. This can make it easier for borrowers to make their payments and avoid default.
Loan consolidation is another option that can help borrowers manage their student loan debt. This involves combining multiple student loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This can make it easier for borrowers to make their payments and save money on interest.
Refinancing is another option that can help borrowers manage their student loan debt. This involves taking out a new loan with a lower interest rate to pay off their existing student loans. This can save borrowers money on interest and help them pay off their debt faster.
These are just a few of the alternative solutions that can help borrowers manage their student loan debt. It is important for borrowers to explore all of their options and choose the solution that is best for their individual situation.
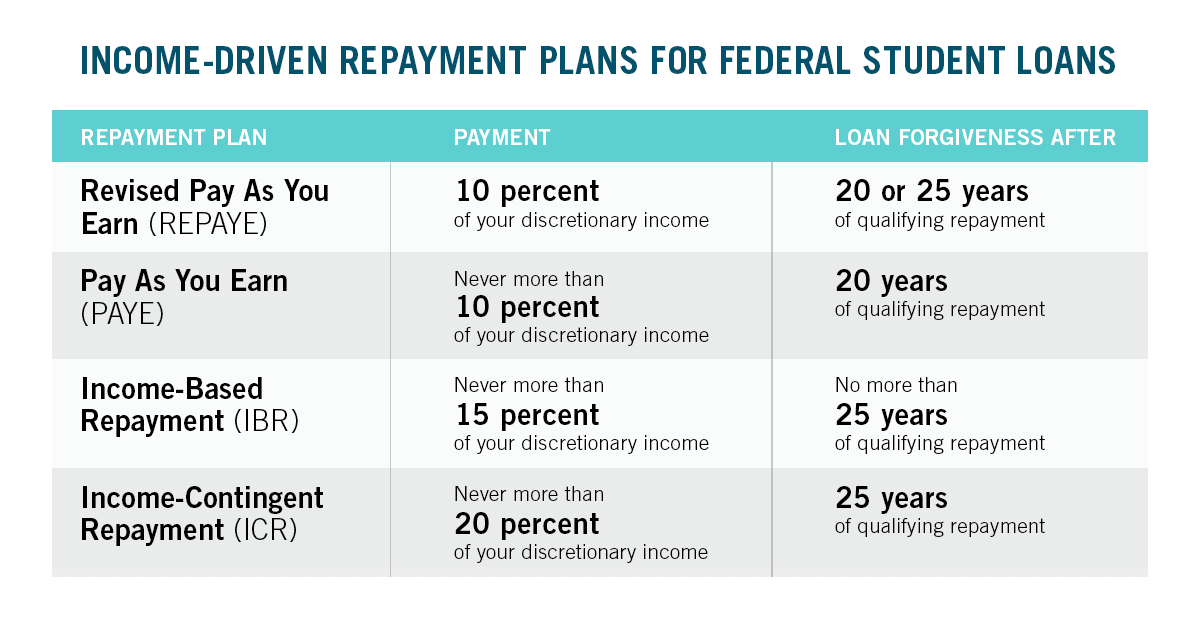
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment plans are a type of federal student loan repayment plan that allows borrowers to make payments based on their income and family size. This can make it easier for borrowers to make their payments and avoid default.
There are four different income-driven repayment plans available:
* Income-Based Repayment (IBR)
* Pay As You Earn (PAYE)
* Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE)
* Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR)
Each of these plans has different eligibility requirements and repayment terms. Borrowers should compare the different plans to see which one is best for their individual situation.
Loan Consolidation
Loan consolidation is the process of combining multiple student loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This can make it easier for borrowers to make their payments and save money on interest.
To consolidate your student loans, you will need to apply with a federal loan servicer. The servicer will review your application and determine if you are eligible for consolidation. If you are approved, the servicer will combine your loans into a single loan with a new interest rate.
The interest rate on your consolidated loan will be a weighted average of the interest rates on your existing loans. The new interest rate will be fixed for the life of the loan.
Refinancing
Refinancing is the process of taking out a new loan with a lower interest rate to pay off your existing student loans. This can save you money on interest and help you pay off your debt faster.
To refinance your student loans, you will need to apply with a private lender. The lender will review your application and determine if you are eligible for refinancing. If you are approved, the lender will give you a new loan with a lower interest rate.
You can use the new loan to pay off your existing student loans. Once your existing loans are paid off, you will only have to make payments on your new loan.
Impact on Higher Education Institutions

Student loan forgiveness has the potential to significantly impact higher education institutions. On the one hand, it could lead to reduced tuition costs, increased enrollment rates, and improved quality of education. On the other hand, it could also lead to decreased revenue for colleges and universities, which could in turn lead to cuts in programs and services.
Tuition Costs
One of the potential benefits of student loan forgiveness is that it could lead to reduced tuition costs. If students know that they will not have to repay their student loans, they may be more likely to attend college and pursue higher degrees. This increased demand for higher education could lead to colleges and universities lowering their tuition costs in order to attract more students.
Enrollment Rates, Save student loan plan
Student loan forgiveness could also lead to increased enrollment rates. If students know that they will not have to repay their student loans, they may be more likely to attend college. This could lead to a more diverse and inclusive student body, as well as a more highly educated workforce.
As you plan your student loan repayment strategy, it’s crucial to assess your options and calculate your monthly payments accurately. Utilize a student loan repayment calculator to estimate your payments based on your loan amount, interest rate, and repayment term.
This tool can empower you to make informed decisions about your repayment plan and explore options to save money on interest.
Quality of Education
Student loan forgiveness could also lead to improved quality of education. If colleges and universities know that they will not have to rely on tuition revenue to fund their operations, they may be more likely to invest in their faculty, staff, and facilities. This could lead to a better learning experience for students.
Ethical Considerations of Student Loan Forgiveness
Student loan forgiveness has sparked debates surrounding ethical considerations, primarily concerning fairness and equity. Some argue that forgiving debt for certain borrowers but not others could be unfair, while others question the potential burden on taxpayers.
One ethical concern is the disparity in treatment among borrowers. Critics argue that forgiving student loans for some but not all creates an unfair advantage. They contend that those who have already repaid their loans or who chose not to pursue higher education due to financial constraints may feel unjustly treated.
Fairness and Equity
- Arguments for fairness: Student loan forgiveness can provide relief to borrowers struggling with debt, promoting economic mobility and reducing financial stress.
- Arguments against fairness: Critics argue that forgiving debt for some but not others is unfair to those who have already repaid their loans or who chose not to pursue higher education due to financial constraints.
Taxpayer Burden
- Arguments for taxpayer burden: Opponents of student loan forgiveness argue that it would place an unfair burden on taxpayers, who would ultimately be responsible for covering the costs of the program.
- Arguments against taxpayer burden: Proponents argue that the economic benefits of student loan forgiveness, such as increased consumer spending and economic growth, would offset the costs to taxpayers.
Legal Challenges to Student Loan Forgiveness
The Biden administration’s student loan forgiveness plan has sparked a legal debate, with opponents arguing that it oversteps the executive branch’s authority and violates the Constitution.
The plan, which would forgive up to $20,000 in federal student loan debt for borrowers earning less than $125,000 per year, relies on a provision in the Higher Education Relief Opportunities for Students Act of 2003 (HEROES Act).
Legal Basis for the Plan
The HEROES Act grants the Secretary of Education broad authority to waive or modify student loan requirements during a national emergency.
The Biden administration argues that the COVID-19 pandemic constitutes a national emergency and that the loan forgiveness plan is necessary to provide relief to borrowers who have been financially impacted by the pandemic.
Arguments Against the Plan
Opponents of the plan argue that the HEROES Act does not provide the Secretary of Education with the authority to forgive student loans on a mass scale.
They also argue that the plan is unfair to taxpayers who have already paid off their student loans or who did not attend college.
Potential Outcomes
The legal challenges to the student loan forgiveness plan are likely to be heard by the Supreme Court.
If the Court strikes down the plan, it will be a major setback for the Biden administration and for borrowers who were hoping to have their student loans forgiven.
Historical Context of Student Loan Forgiveness
Student loan forgiveness programs have a long and complex history in the United States. The first federal student loan forgiveness program was established in 1965 as part of the Higher Education Act. This program provided loan forgiveness to teachers who worked in low-income schools for five years. Since then, several other student loan forgiveness programs have been created, including the Public Service Loan Forgiveness Program (PSLF) and the Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program.
The PSLF program was created in 2007 to encourage individuals to work in public service by providing them with loan forgiveness after 10 years of service. The Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program was created in 1998 to provide loan forgiveness to teachers who work in low-income schools for five years. These programs have been successful in helping to reduce the burden of student loan debt for many individuals.
Key Factors Influencing Student Loan Forgiveness Policies
- The rising cost of higher education
- The increasing number of students who are graduating with student loan debt
- The difficulty that many borrowers are having in repaying their student loans
- The political and economic debates surrounding student loan forgiveness
The rising cost of higher education has made it increasingly difficult for students to afford college without taking on student loans. The increasing number of students who are graduating with student loan debt has put a strain on the federal student loan system. The difficulty that many borrowers are having in repaying their student loans has led to calls for student loan forgiveness.
The political and economic debates surrounding student loan forgiveness are complex. Some people argue that student loan forgiveness is necessary to help borrowers who are struggling to repay their loans. Others argue that student loan forgiveness is unfair to taxpayers who have already repaid their loans. The debate over student loan forgiveness is likely to continue for many years to come.
Different Perspectives on the Potential Impact of Student Loan Forgiveness
There are a variety of different perspectives on the potential impact of student loan forgiveness. Some people argue that student loan forgiveness would have a positive impact on the economy by stimulating spending and economic growth. Others argue that student loan forgiveness would have a negative impact on the economy by increasing the national debt. There is also debate about the potential impact of student loan forgiveness on individuals and institutions.
Some people argue that student loan forgiveness would have a positive impact on individuals by reducing their debt burden and allowing them to save more money. Others argue that student loan forgiveness would have a negative impact on individuals by reducing the incentive to repay student loans. There is also debate about the potential impact of student loan forgiveness on institutions, such as colleges and universities.
International Comparisons of Student Loan Forgiveness
Countries worldwide have implemented various student loan forgiveness programs to address the rising burden of student debt. By examining these programs, we can gain valuable insights into their effectiveness and potential implications for the United States.
United Kingdom
The UK introduced an income-driven repayment plan in 2012. Under this plan, graduates repay their loans based on their income and any outstanding balance is forgiven after 30 years. This plan has been criticized for its long repayment period and low forgiveness rate.
Canada
Canada offers a Loan Forgiveness Program for borrowers who work in full-time public service jobs for 10 years. This program has been successful in attracting and retaining qualified individuals in public sector roles.
Australia
Australia has a Higher Education Loan Program (HELP) that allows students to defer loan repayments until they reach a certain income threshold. The loans are forgiven after 25 years or if the borrower becomes permanently disabled.
New Zealand
New Zealand offers an Income-Contingent Loan scheme that bases loan repayments on income. After 10 years of repayment, any remaining balance is forgiven. This scheme has been praised for its simplicity and effectiveness.
Germany
Germany provides interest-free student loans to undergraduate students. Repayment begins after graduation and is based on income. After 20 years of repayment, any outstanding balance is forgiven.
France
France offers a debt cancellation program for low-income borrowers. Borrowers who earn below a certain income threshold can have their student loans forgiven after 15 years of repayment.
Public Perception of Student Loan Forgiveness

Student loan forgiveness has been a topic of intense debate in recent years, with strong opinions on both sides of the issue. To better understand public perception of this complex issue, a survey was conducted to gather data on the level of support and concerns among different demographic groups.
The survey results revealed that a majority of respondents support some form of student loan forgiveness. However, there is a significant variation in support levels based on factors such as age, income, and political affiliation. Younger respondents and those with higher levels of student debt are more likely to support forgiveness, while older respondents and those with lower levels of debt are more likely to oppose it.
Concerns about Student Loan Forgiveness
While there is general support for student loan forgiveness, there are also concerns about its potential impact. Some respondents expressed concerns about the cost of forgiveness, arguing that it would be unfair to taxpayers who have already paid off their own student loans or who do not have college degrees. Others worried that forgiveness would encourage colleges and universities to raise tuition prices, knowing that the government would ultimately be responsible for paying off the loans.
Support for Student Loan Forgiveness
Despite these concerns, there are also strong arguments in favor of student loan forgiveness. Supporters argue that it would provide much-needed relief to borrowers who are struggling to repay their loans. They also argue that it would stimulate the economy by freeing up money that borrowers could spend on other goods and services.
Design an Infographic on Student Loan Forgiveness
Student loan forgiveness has been a hot topic in recent years, as the cost of higher education continues to rise. An infographic can be a great way to visualize the key information about the student loan forgiveness plan and make it more accessible to the public.
Types of Loans Eligible for Forgiveness
- Federal student loans
- Perkins loans
- Defaulted student loans
Timeline for Forgiveness
The timeline for forgiveness will vary depending on the type of loan and the forgiveness program. However, in general, borrowers can expect to see forgiveness within 20-25 years of repayment.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Who is eligible for student loan forgiveness?
- What are the different types of student loan forgiveness programs?
- How do I apply for student loan forgiveness?
Student Loan Forgiveness Timeline
The student loan forgiveness plan has undergone several key developments since its inception. Here’s a timeline outlining the major events that have shaped its progress:
Planning and Development
- 2020: Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden unveils a proposal for student loan forgiveness during his campaign.
- 2021: President Biden takes office and includes student loan forgiveness as part of his economic recovery plan.
- April 2022: The Biden administration announces plans to forgive $10,000 in student loan debt for borrowers earning less than $125,000 per year.
Implementation and Challenges
- August 2022: The Biden administration releases an application for student loan forgiveness.
- October 2022: A federal appeals court blocks the implementation of the forgiveness plan, citing legal challenges.
- November 2022: The Supreme Court agrees to hear arguments on the legality of the plan.
Legal Challenges and Future Prospects
The student loan forgiveness plan continues to face legal challenges, with the Supreme Court set to rule on its legality in the coming months. The outcome of these challenges will determine the future of the plan and its impact on millions of student loan borrowers.
Epilogue
As the Save Student Loan Plan continues to evolve, it is imperative that we engage in thoughtful discussions about its implications for individuals, institutions, and the economy as a whole. By understanding the complexities of the plan and its potential impact, we can work together to create a more equitable and sustainable system of higher education financing.
Let us continue to advocate for policies that prioritize affordability, accessibility, and fairness in higher education. Together, we can empower future generations to pursue their educational aspirations without the crushing burden of student loan debt.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the eligibility criteria for the Save Student Loan Plan?
The eligibility criteria for the Save Student Loan Plan are still under development and may vary depending on the specific implementation of the plan. However, it is anticipated that the plan will prioritize individuals with high levels of student loan debt relative to their income and those who have been struggling to make payments.
What are the potential benefits of the Save Student Loan Plan?
The potential benefits of the Save Student Loan Plan are significant. For individuals, the plan could provide much-needed financial relief, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. On a broader scale, the plan could stimulate economic growth by increasing consumer spending and investment.
What are the challenges and limitations of the Save Student Loan Plan?
The Save Student Loan Plan faces several challenges and limitations. Concerns have been raised about the potential cost of the plan, its impact on the higher education system, and the fairness of forgiving student loan debt for some borrowers but not others.

