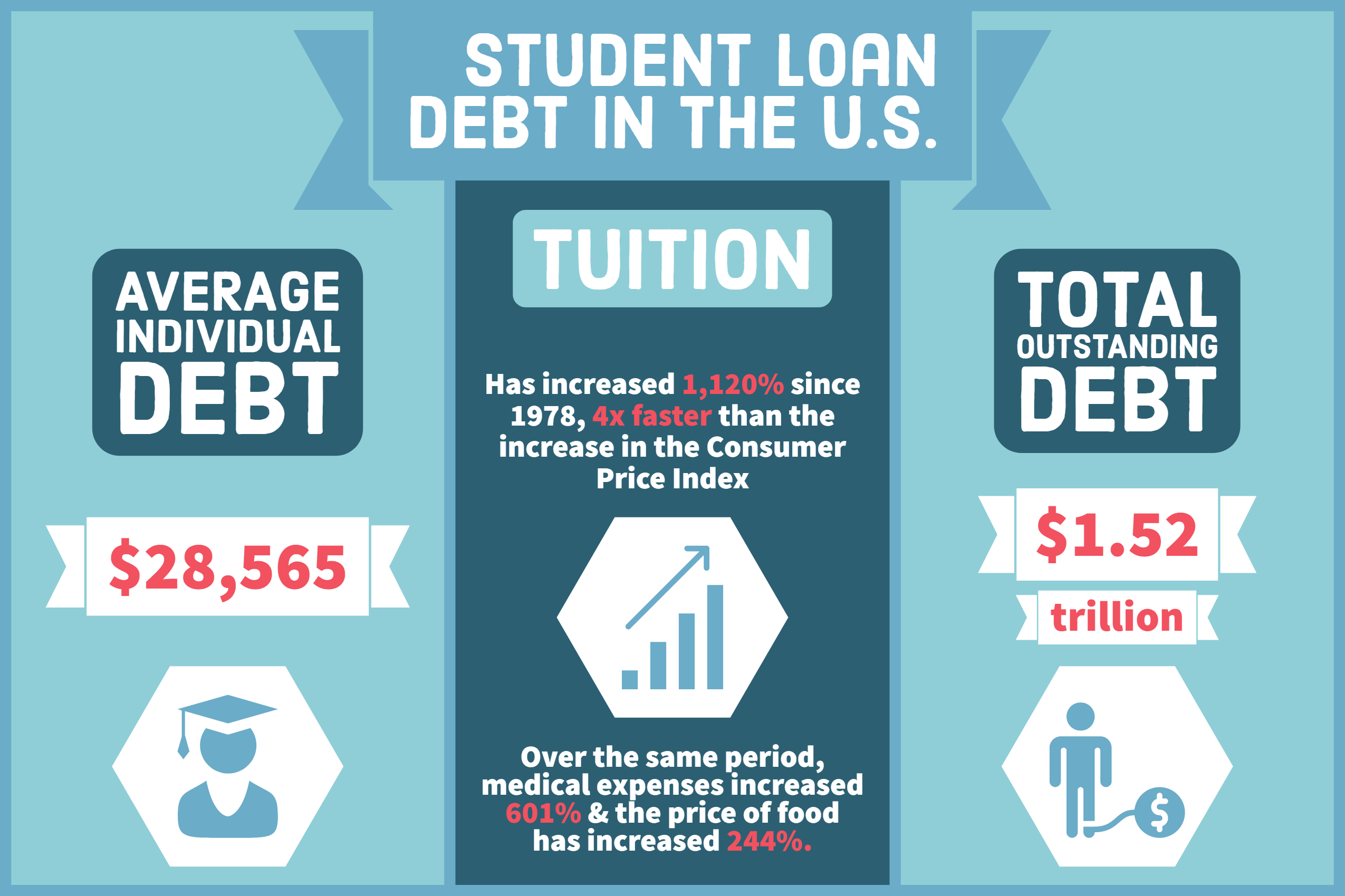
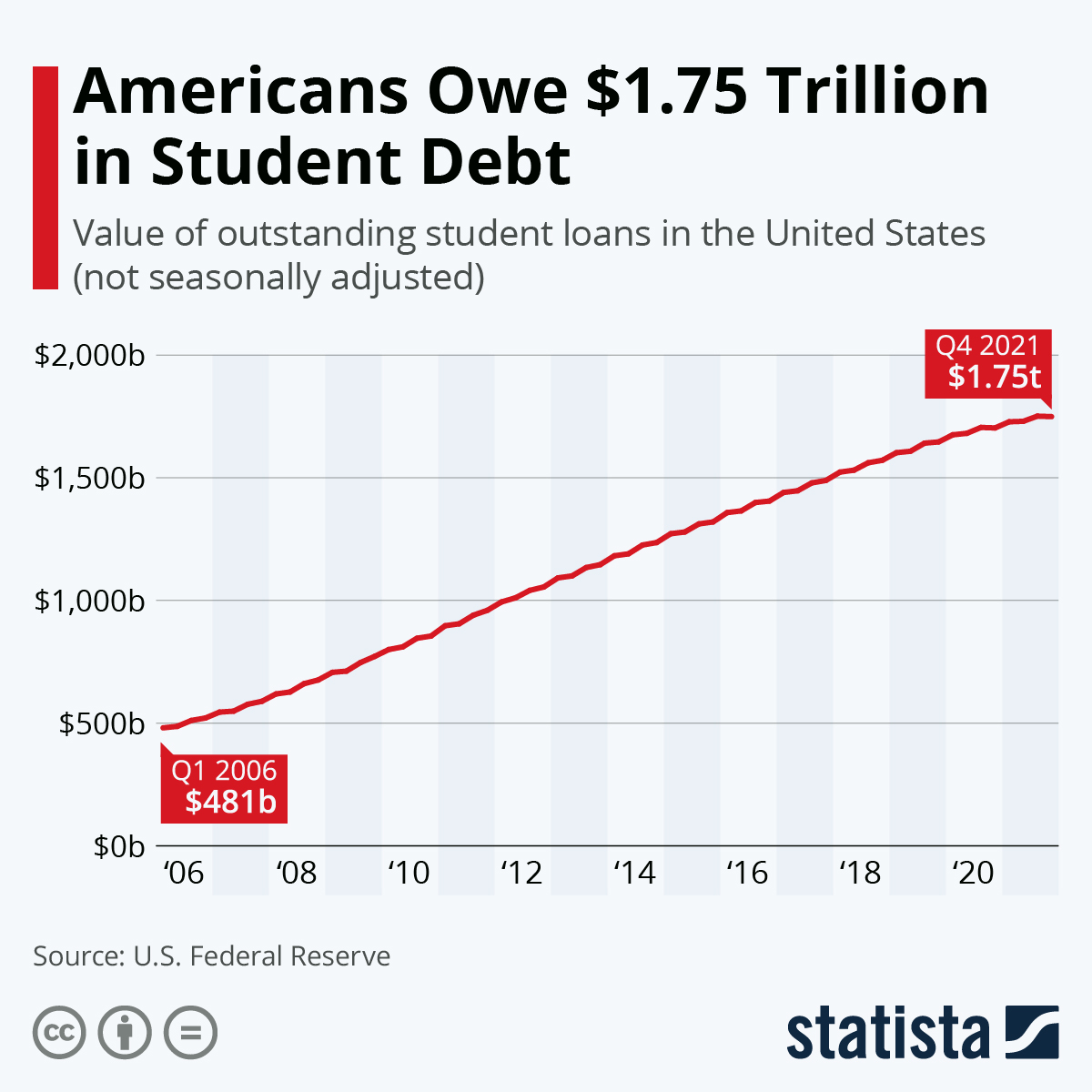
Student loan debt has become a pressing issue, affecting millions of Americans and weighing heavily on their financial well-being. With outstanding debt exceeding $1.7 trillion, it’s time to delve into the complexities of this crisis, exploring its impact on individuals, the economy, and society as a whole.
From crushing financial burdens to compromised mental health, student loan debt is taking a toll on individuals. It hinders career choices, delays major life decisions, and perpetuates economic inequality. Moreover, the systemic issues surrounding student lending demand critical examination.
Impact of Student Loan Debt on Individuals
Student loan debt has become a major financial burden for millions of individuals, with far-reaching consequences that extend beyond financial strain. This essay will explore the impact of student loan debt on individuals, examining its financial, mental, and career-related implications.
The burden of student loan debt weighs heavily on the minds of millions of Americans. But there’s a glimmer of hope: the latest student loan forgiveness update brings encouraging news for those struggling with their student loan payments. While the details of the update are still emerging, it offers a potential path to financial relief for countless individuals facing the weight of student loan debt.
Financial Burden
- High monthly payments can strain budgets, making it difficult to afford other essential expenses such as housing, food, and healthcare.
- Interest charges can accumulate over time, significantly increasing the total amount owed.
- Student loan debt can delay or prevent individuals from saving for retirement or purchasing a home.
Mental Health and Well-being
- The financial stress associated with student loan debt can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
- The stigma surrounding student loan debt can also contribute to feelings of shame and isolation.
- The burden of student loan debt can affect sleep quality, relationships, and overall well-being.
Career Choices and Life Decisions
- Individuals with high student loan debt may be more likely to choose lower-paying jobs that offer loan forgiveness programs.
- Student loan debt can delay or prevent individuals from pursuing graduate education or starting their own businesses.
- The financial burden of student loan debt can also affect decisions about marriage, having children, and buying a home.
Case Study
A recent study by the National Center for Education Statistics found that the average student loan debt for the class of 2020 was $28,400. This represents a 25% increase from the average debt for the class of 2010.
The study also found that student loan debt is disproportionately affecting certain groups of individuals. For example, Black and Hispanic borrowers have higher average student loan debt than white borrowers.
Economic Consequences of Student Loan Debt

Student loan debt has become a major financial burden for millions of Americans, with the total amount owed surpassing $1.7 trillion. This staggering figure has a significant impact on the economy, affecting job growth, economic inequality, and the overall financial well-being of individuals.
Impact on Job Growth
The high cost of student loans can discourage individuals from pursuing higher education, limiting the pool of skilled workers available to businesses. This can lead to slower job growth and a less competitive economy.
Impact on Economic Inequality
Student loan debt disproportionately affects low-income and minority borrowers. These individuals are more likely to take on higher levels of debt and struggle to repay it, leading to a widening gap in wealth and economic opportunities.
Potential Benefits of Reducing or Eliminating Student Loan Debt
Reducing or eliminating student loan debt could have several positive economic benefits. It would free up disposable income for individuals, allowing them to spend more on goods and services, boosting economic growth. Additionally, it would reduce the burden on taxpayers who subsidize student loans through government programs.
Government Involvement in Student Loan Lending
The federal government plays a significant role in student lending through various programs that provide loans to students pursuing higher education. These programs aim to increase access to higher education and reduce the financial burden on students and their families.
Federal Student Loan Programs
The federal government offers several types of student loans through the Federal Direct Loan Program:
– Direct Subsidized Loans: Available to undergraduate students with financial need, based on the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). The government pays the interest on these loans while the student is in school.
– Direct Unsubsidized Loans: Available to both undergraduate and graduate students, regardless of financial need. The student is responsible for paying the interest on these loans, even while in school.
– Direct PLUS Loans: Available to graduate students and parents of dependent undergraduate students. These loans have higher interest rates than Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans.
State Student Loan Programs
In addition to federal programs, many states offer their own student loan programs. These programs typically provide loans to students who are residents of the state. The terms and conditions of state student loans can vary widely.
Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for federal or state student loans, students must meet certain requirements, including:
– Be enrolled in an accredited college or university.
– Be a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen.
– Have a valid Social Security number.
– Not be in default on any federal student loans.
Interest Rates
The interest rates on federal student loans are set by law. The rates for Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans are currently 4.99% for undergraduate loans and 6.54% for graduate loans. The interest rate for Direct PLUS Loans is currently 7.54%. State student loan programs may have different interest rates.
Alternative Funding Models for Higher Education
The rising cost of higher education has made it increasingly difficult for students to finance their education without taking on significant amounts of debt. As a result, there is growing interest in alternative funding models that could make college more affordable and reduce the burden of student loan debt.
One alternative funding model is the income-share agreement (ISA). Under an ISA, students agree to pay a percentage of their future income for a fixed period of time in exchange for upfront funding to cover the cost of their education. ISAs have the potential to make college more affordable for students by reducing the amount of debt they have to take on and by providing them with more flexibility in how they repay their loans.
Another alternative funding model is debt-free college. Under a debt-free college program, students attend college for free and then repay the cost of their education through a percentage of their future income. Debt-free college programs have the potential to make college more affordable for students by eliminating the need for them to take on any debt.
Employer-sponsored tuition assistance is another alternative funding model that can help students to finance their education. Under employer-sponsored tuition assistance programs, employers provide financial assistance to their employees to help them pay for the cost of college. Employer-sponsored tuition assistance programs can make college more affordable for students by reducing the amount of debt they have to take on and by providing them with more flexibility in how they repay their loans.
Comparison of Alternative Funding Models, Student loan debt
The following table compares the advantages and disadvantages of different alternative funding models for higher education:
| Funding Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Income-Share Agreements |
|
|
| Debt-Free College |
|
|
| Employer-Sponsored Tuition Assistance |
|
|
Potential Impact of Alternative Funding Models on Student Loan Debt
Alternative funding models have the potential to significantly reduce the amount of student loan debt that students have to take on. A study by the Brookings Institution found that if all students were to use ISAs to finance their education, the total amount of student loan debt in the United States would be reduced by $1 trillion.
In addition to reducing the amount of student loan debt, alternative funding models can also make college more affordable for students. A study by the College Board found that students who used ISAs to finance their education saved an average of $10,000 on the cost of their education.
Examples of Alternative Funding Models in Practice
There are a number of colleges and universities that have implemented alternative funding models. For example, Purdue University offers an ISA program called Back a Boiler. Under the Back a Boiler program, students agree to pay a percentage of their future income for a fixed period of time in exchange for upfront funding to cover the cost of their education. The University of Southern California offers a debt-free college program called the USC Trojan Scholarship Fund. Under the USC Trojan Scholarship Fund, students attend college for free and then repay the cost of their education through a percentage of their future income.
Role of Government and Philanthropic Organizations
Government and philanthropic organizations can play a role in supporting alternative funding models for higher education. For example, the government could provide grants to colleges and universities that implement alternative funding models. Philanthropic organizations could provide scholarships to students who use alternative funding models to finance their education.
Argument for the Adoption of a Specific Alternative Funding Model
I believe that the government should adopt a debt-free college program for all students. Debt-free college programs have the potential to make college more affordable for students, reduce the amount of student loan debt that students have to take on, and increase the number of students who are able to attend college. I believe that the benefits of debt-free college programs outweigh the costs and that the government should make this investment in the future of our country.
Student loan debt can be a major burden for many graduates. To help manage this debt, consider using a student loan calculator . This tool can help you estimate your monthly payments, total interest paid, and repayment period. By understanding the full scope of your student loan debt, you can make informed decisions about repayment options and financial planning.
Student Loan Repayment Options: Student Loan Debt

Managing student loan debt can be overwhelming, but there are various repayment plans available to help you manage your payments and reach your financial goals. Understanding the different options and choosing the one that suits your individual circumstances is crucial for effective debt repayment.
Types of Repayment Plans
There are four main types of student loan repayment plans:
- Standard Repayment Plan: The most straightforward plan, with fixed monthly payments that repay the loan in 10 years.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: Similar to the Standard Plan, but with smaller initial payments that gradually increase over time.
- Extended Repayment Plan: Allows for longer repayment terms of up to 25 years, resulting in lower monthly payments but potentially higher total interest.
- Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans: Adjust monthly payments based on your income and family size, potentially reducing payments significantly.
Choosing the Best Repayment Plan
The best repayment plan for you depends on several factors:
- Loan amount: Higher loan amounts may require longer repayment terms or higher monthly payments.
- Income: Your income determines the eligibility for IDR plans and the amount you can afford to repay.
- Expenses: Consider your monthly expenses to ensure the repayment plan fits your budget.
- Career goals: If you anticipate higher earnings in the future, you may choose a plan with lower initial payments.
Loan Forgiveness and Discharge
In certain cases, you may be eligible for loan forgiveness or discharge, which can eliminate your student loan debt:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Forgives student loans after 10 years of working full-time in public service.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness: Forgives up to $17,500 in student loans for teachers who work in low-income schools.
- Disability Discharge: Discharges student loans if you become totally and permanently disabled.
- Death Discharge: Discharges student loans if the borrower dies.
| Repayment Plan | Monthly Payment | Loan Term | Interest Rate | Eligibility Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Repayment Plan | Fixed | 10 years | Fixed | None |
| Graduated Repayment Plan | Lower initial payments that increase over time | 10 years | Fixed | None |
| Extended Repayment Plan | Lower monthly payments | Up to 25 years | Fixed | Loan amount over $30,000 |
| Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans | Payments based on income and family size | 20-25 years | Variable | Income below certain limits |
Impact of Repayment Plans
The choice of repayment plan can significantly impact the total cost of your loan and the time it takes to repay it:
- IDR plans can reduce monthly payments but extend the loan term, potentially increasing the total interest paid.
- Extended Repayment Plans lower monthly payments but can result in paying more interest over time.
- Standard and Graduated Repayment Plans have shorter loan terms but higher monthly payments.
Applying for Loan Forgiveness or Discharge
To apply for loan forgiveness or discharge, you must submit the appropriate forms and documentation to your loan servicer:
- PSLF: Public Service Loan Forgiveness Application
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness: Teacher Loan Forgiveness Application
- Disability Discharge: Disability Discharge Application
- Death Discharge: Death Discharge Application
Strategies for Managing Student Loan Debt
Managing student loan debt effectively requires a comprehensive approach that involves creating a budget, tracking expenses, and exploring repayment options. By implementing these strategies, individuals can reduce the burden of their student loans and achieve financial stability.
The crushing weight of student loan debt can leave graduates feeling overwhelmed and hopeless. However, the biden student loan debt relief program offers a glimmer of hope, providing much-needed assistance to those struggling with the burden of their education costs.
By tackling this issue head-on, the government is taking a step towards alleviating the financial stress that has plagued countless graduates, allowing them to focus on building their careers and contributing to society without the weight of overwhelming debt.
Creating a Budget and Tracking Expenses
Creating a budget is crucial for managing student loan debt. It allows you to track your income and expenses, ensuring that you allocate funds wisely. Start by listing all your sources of income, including wages, scholarships, and grants. Then, list your fixed expenses, such as rent, utilities, and car payments. Finally, track your variable expenses, such as groceries, entertainment, and dining out. Once you have a clear understanding of your cash flow, you can allocate funds to your student loan payments.
Negotiating with Lenders
If you are struggling to make your student loan payments, do not hesitate to contact your lender. Many lenders are willing to work with borrowers to find a solution that fits their financial situation. You may be able to negotiate a lower interest rate, extend the loan term, or put your loans into forbearance or deferment. It is important to be honest and upfront with your lender about your financial situation and to provide documentation to support your request.
Exploring Debt Consolidation Options
Debt consolidation can be a viable option for borrowers who have multiple student loans with different interest rates and due dates. By consolidating your loans, you can combine them into a single loan with a fixed interest rate and monthly payment. This can simplify your repayment process and potentially save you money on interest. However, it is important to compare the terms of your new loan with your existing loans before consolidating to ensure that you are getting a better deal.
Student Loan Debt and Social Justice

Student loan debt has a disproportionate impact on marginalized communities, exacerbating existing inequalities and hindering economic mobility.
Factors such as race, gender, and socioeconomic status play a significant role in determining student loan debt outcomes. Studies have shown that Black and Hispanic borrowers have higher levels of student loan debt compared to White borrowers, even after controlling for factors like college major and family income.
Student loan debt can be a heavy burden for many, impacting their financial stability and future plans. The Biden student loan forgiveness program aims to alleviate this burden, providing relief to borrowers and potentially opening up new opportunities for them.
While the full impact of this program is yet to be seen, it represents a significant step towards addressing the challenges posed by student loan debt.
Role of Race
- Black borrowers are more likely to attend for-profit colleges, which have higher tuition costs and lower graduation rates, leading to higher student loan debt.
- Black borrowers also face discrimination in the labor market, resulting in lower earning potential and making it harder to repay student loans.
Role of Gender
- Women borrow more for higher education than men, and they also tend to earn less, making it more difficult to repay student loans.
- Women are more likely to take on caregiving responsibilities, which can interrupt their careers and reduce their earning potential.
Role of Socioeconomic Status
- Students from low-income families are more likely to take on student loans to cover the cost of college.
- They are also more likely to attend underfunded schools with fewer resources, which can limit their career opportunities and earning potential.
Student Loan Debt: A Burden on Individuals and the Economy
Student loan debt has become a major financial burden for millions of Americans. The total amount of student loan debt in the United States has surpassed $1.7 trillion, and the average amount owed by borrowers is over $30,000. This debt has a significant impact on the economy, as it reduces consumer spending and slows economic growth.
Impact of Student Loan Debt on Individuals
Student loan debt can have a devastating impact on individuals. It can delay major life milestones, such as buying a home or starting a family. It can also make it difficult to save for retirement or pay off other debts. In some cases, student loan debt can even lead to bankruptcy.
Economic Consequences of Student Loan Debt
Student loan debt also has a negative impact on the economy. It reduces consumer spending, as borrowers are forced to allocate a significant portion of their income to repaying their loans. This can lead to a slowdown in economic growth. In addition, student loan debt can make it more difficult for businesses to hire and retain qualified workers.
Student Loan Debt in Pop Culture
Student loan debt has become a prevalent issue in modern society, and its cultural significance has been reflected in various forms of popular culture. From movies and TV shows to music, student loan debt is often portrayed as a burden that weighs heavily on individuals, shaping their life choices and societal attitudes.
Movies and TV Shows
In the movie “The Big Short,” student loan debt is depicted as a contributing factor to the 2008 financial crisis. The film highlights the role of subprime mortgages and predatory lending practices that targeted college graduates with high levels of student debt.
Similarly, the TV show “Girls” features a character named Hannah Horvath who struggles to repay her student loans while pursuing her dream of becoming a writer. The show explores the emotional and financial toll that student loan debt can take on individuals, particularly those from low-income backgrounds.
Music
Student loan debt has also found its way into music, with artists like Taylor Swift and Kendrick Lamar addressing the issue in their songs. Swift’s song “All Too Well (10 Minute Version)” includes the lyrics “Student loans and sleepless nights, ’cause I stayed up trying to pay my way through your school,” capturing the financial and emotional burdens of student debt.
Kendrick Lamar’s song “Alright” features the line “Student loans got me stressed out,” reflecting the widespread anxiety and frustration associated with student debt among young adults.
Cultural Significance
The portrayal of student loan debt in popular culture has significant cultural implications. It raises awareness about the issue, normalizes the conversation surrounding it, and challenges societal attitudes towards education and debt.
By showcasing the personal stories of individuals struggling with student loan debt, popular culture helps to humanize the issue and make it relatable to a broader audience. This can lead to increased empathy and understanding, as well as a shift in public opinion towards supporting policies that address the student loan debt crisis.
Student Loan Debt and Personal Finance
Student loan debt can have a significant impact on personal finance decisions, making it more difficult to save for retirement, buy a home, or reach other financial goals. Understanding how to manage student loan debt effectively is crucial for individuals seeking financial stability.
Balancing Student Loan Repayment with Other Financial Goals
- Create a budget: Track income and expenses to identify areas where spending can be reduced to allocate more funds towards student loan repayment.
- Prioritize high-interest debt: Focus on paying off student loans with the highest interest rates first to minimize interest charges.
- Consider refinancing: Explore refinancing options to secure a lower interest rate, potentially reducing monthly payments and saving money in the long run.
- Utilize tax benefits: Take advantage of tax deductions or credits available for student loan interest payments.
- Seek financial assistance: If struggling to make payments, contact the loan servicer or explore income-driven repayment plans that adjust payments based on income.
Importance of Financial Literacy for Individuals with Student Loan Debt
- Understanding loan terms: Knowing the interest rate, repayment period, and other loan details is essential for effective management.
- Managing cash flow: Budgeting and planning for student loan payments ensures financial stability and prevents missed payments.
- Making informed decisions: Financial literacy empowers individuals to make wise choices about student loan repayment options, refinancing, and other financial strategies.
- Long-term financial planning: Student loan debt can impact long-term financial goals, such as retirement savings and homeownership. Understanding the implications helps individuals plan accordingly.
- Seeking professional advice: If needed, consult with a financial advisor to develop a personalized plan that aligns with individual circumstances and goals.
Student Loan Debt and the Future of Higher Education

Student loan debt has become an increasingly pressing issue in recent years, and it is likely to have a significant impact on the future of higher education. The high cost of college has made it necessary for many students to take on large amounts of debt in order to finance their education. This debt can have a number of negative consequences for individuals, including:
- Difficulty finding a job
- Lower earnings
- Delayed homeownership
- Increased risk of default
In addition to the individual consequences, student loan debt can also have negative consequences for the economy as a whole. The high cost of college can discourage people from pursuing higher education, which can lead to a shortage of skilled workers. Student loan debt can also reduce consumer spending, which can slow economic growth.
There are a number of things that can be done to address the challenges posed by student loan debt. One approach is to make college more affordable. This can be done by increasing government funding for higher education, providing more financial aid to students, and making it easier for students to refinance their loans. Another approach is to help students manage their debt more effectively. This can be done by providing counseling and financial education, and by making it easier for students to consolidate their loans.
The future of higher education is uncertain, but it is clear that student loan debt will be a major factor in shaping its future. It is important to address the challenges posed by student loan debt in order to ensure that higher education remains accessible and affordable for all students.
Innovative Approaches to Address the Challenges Posed by Student Loan Debt
There are a number of innovative approaches that can be used to address the challenges posed by student loan debt. These approaches include:
- Income-driven repayment plans
- Loan forgiveness programs
- Student loan refinancing
- Debt consolidation
These approaches can help students manage their debt more effectively and reduce the overall burden of student loan debt.
Student Loan Debt and the Economy

Student loan debt has become a major issue in the United States, with over $1.7 trillion in outstanding loans. This debt is disproportionately held by low-income borrowers and borrowers of color, and it has a significant impact on the economy.
Data Analysis
* The total amount of student loan debt in the U.S. is over $1.7 trillion.
* The average student loan debt for a bachelor’s degree recipient is $28,950.
* The median student loan debt for a bachelor’s degree recipient is $17,100.
* Student loan debt is disproportionately held by low-income borrowers and borrowers of color.
* Black borrowers have an average student loan debt of $25,000, compared to $18,000 for white borrowers.
* Hispanic borrowers have an average student loan debt of $23,000, compared to $18,000 for white borrowers.
* Student loan debt has a significant impact on the economy.
* Student loan debt reduces job growth by making it more difficult for graduates to start businesses.
* Student loan debt reduces wage growth by making it more difficult for graduates to negotiate higher salaries.
* Student loan debt increases economic inequality by making it more difficult for low-income borrowers to build wealth.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Reducing or Eliminating Student Loan Debt
There are a number of potential benefits to reducing or eliminating student loan debt.
* Reducing or eliminating student loan debt would increase job growth by making it easier for graduates to start businesses.
* Reducing or eliminating student loan debt would increase wage growth by making it easier for graduates to negotiate higher salaries.
* Reducing or eliminating student loan debt would reduce economic inequality by making it easier for low-income borrowers to build wealth.
However, there are also some potential risks to reducing or eliminating student loan debt.
* Reducing or eliminating student loan debt would increase the federal budget deficit.
* Reducing or eliminating student loan debt would reduce the availability of credit for future students.
Student Loan Debt and Social Policy
Student loan debt has become a significant issue in many countries, with far-reaching social and economic consequences. It can hinder individuals’ financial stability, limit their economic mobility, and exacerbate existing social inequalities. Governments have a crucial role in addressing these challenges by implementing policies that reduce the burden of student loan debt and promote economic equity.
Government Intervention
Governments can intervene in the student loan market in various ways to mitigate the negative impacts of student loan debt. These interventions can include:
– Income-driven repayment plans: These plans adjust monthly payments based on the borrower’s income, making repayment more manageable for those with lower earnings.
– Loan forgiveness programs: These programs provide complete or partial cancellation of student loan debt after a certain number of years of service in certain fields, such as education or healthcare.
– Interest rate subsidies: Governments can subsidize interest rates on student loans, reducing the overall cost of borrowing for students.
– Tuition assistance programs: Governments can provide grants or scholarships to help students cover the cost of tuition, reducing the need for student loans.
Ultimate Conclusion
Addressing the student loan debt crisis requires a multifaceted approach. Government policies, alternative funding models, and personal financial strategies all play a role in mitigating its impact. By raising awareness, advocating for change, and empowering individuals with knowledge, we can work towards a future where higher education is accessible without the burden of crippling debt.
Popular Questions
What are the different types of student loan repayment plans available?
There are several repayment plans available, including Standard, Graduated, Extended, and Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans, each with varying monthly payments, loan terms, and interest rates.
What are the options for student loan forgiveness or discharge?
Forgiveness options include Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Teacher Loan Forgiveness, Disability Discharge, and Death Discharge, each with specific eligibility criteria and application processes.
How can I manage student loan debt effectively?
Effective management strategies include creating a budget, negotiating with lenders, exploring debt consolidation, and seeking professional financial advice if needed.

