The Problem & Opportunities of Business Analysts is a fascinating topic that invites us on a journey to explore the challenges and opportunities faced by these professionals. Business Analysts play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between business needs and technological solutions, but their work is not without its complexities. Join us as we delve into the intricate world of Business Analysis, uncovering the obstacles they face and the immense potential they hold.
In this comprehensive guide, we will navigate the landscape of Business Analysis, examining the core skills and competencies required for success. We will explore the latest trends and technologies shaping the profession, and delve into the ethical considerations that guide their work. Whether you’re a seasoned Business Analyst or aspiring to enter this dynamic field, this guide will provide valuable insights and practical advice to help you thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Problem Statement: Problem & Opportunities Of Business Analyst
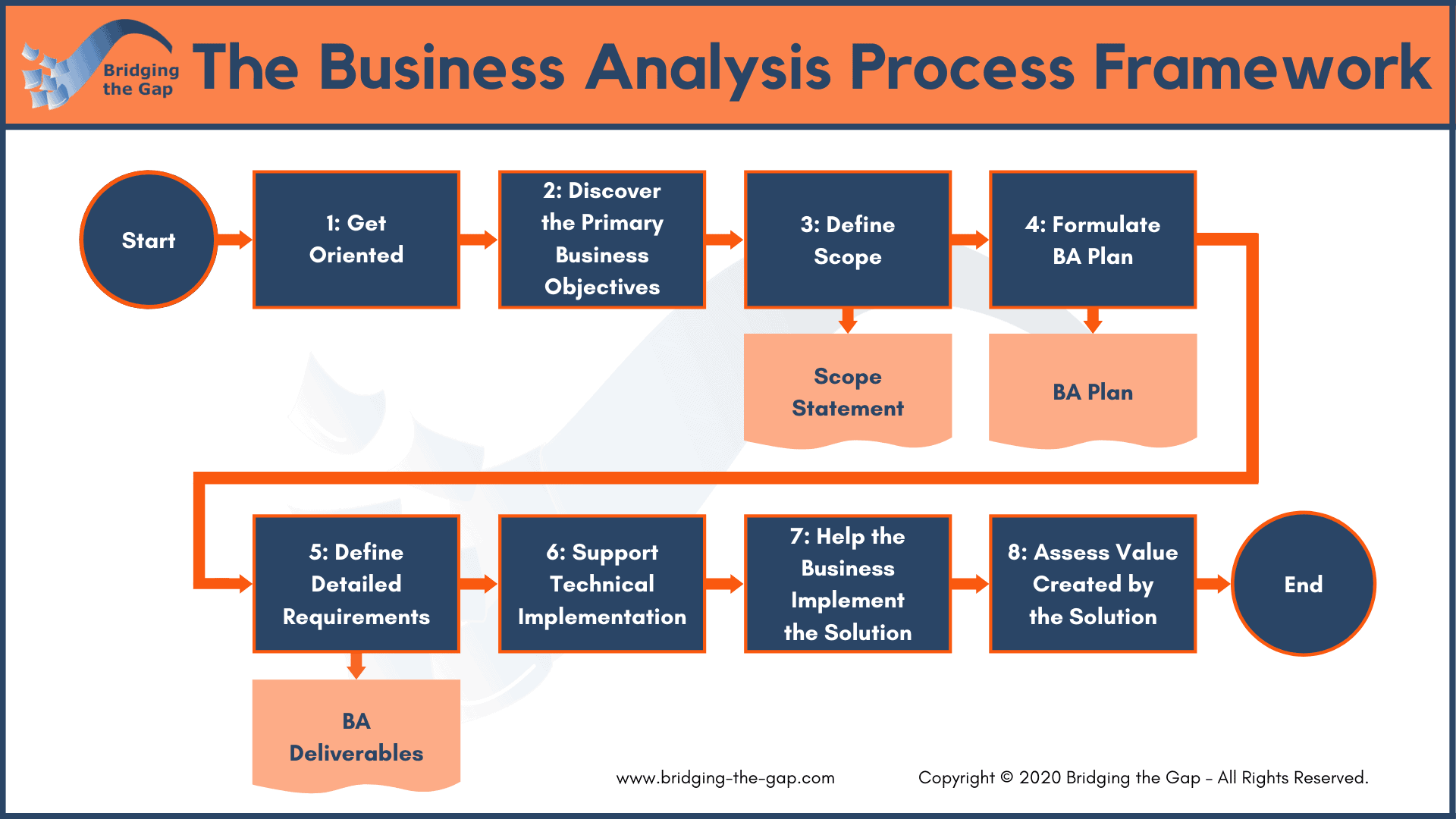
Business Analysts (BAs) play a critical role in bridging the gap between business needs and technical solutions. However, they often face a range of challenges that can hinder their effectiveness.
One of the most common challenges is the lack of clear and concise requirements. This can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and costly rework. Another challenge is the rapidly changing business landscape. BAs must be able to adapt quickly to new technologies, regulations, and market trends.
Impact of Challenges
The challenges faced by BAs can have a significant impact on business operations and decision-making. Poorly defined requirements can lead to the development of systems that do not meet the needs of the business. This can result in lost productivity, wasted resources, and missed opportunities.
The rapidly changing business landscape can also make it difficult for BAs to keep up with the latest trends. This can lead to them making recommendations that are based on outdated information. As a result, businesses may miss out on opportunities to improve their operations or gain a competitive advantage.
Industry Trends

The role of Business Analysts is constantly evolving, driven by emerging trends and technologies. These advancements are shaping the profession, creating new opportunities and challenges for Business Analysts.
One of the most significant trends is the rise of big data and analytics. Businesses are collecting vast amounts of data, and Business Analysts are playing a crucial role in transforming this data into actionable insights. They are using data visualization tools, statistical analysis techniques, and machine learning algorithms to uncover patterns, identify trends, and make predictions.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The proliferation of data has made data-driven decision making essential for businesses. Business Analysts are leveraging data to understand customer behavior, optimize business processes, and identify new opportunities for growth. They are collaborating with data scientists and other technical experts to develop data-driven solutions that address business challenges.
Agile Development
Agile development methodologies are becoming increasingly popular, and Business Analysts are adapting their practices to align with agile principles. They are working closely with development teams to gather requirements, prioritize features, and ensure that the final product meets business needs. Business Analysts are also playing a key role in DevOps initiatives, which aim to improve collaboration between development and operations teams.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is transforming the way businesses operate, and Business Analysts are exploring the opportunities and challenges it presents. They are helping organizations to migrate to the cloud, optimize cloud usage, and develop cloud-based applications. Business Analysts are also working with cloud providers to develop new services and solutions that meet the evolving needs of businesses.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly changing the business landscape, and Business Analysts are at the forefront of this transformation. They are exploring the potential of AI to automate tasks, improve decision making, and create new products and services. Business Analysts are working with AI engineers to develop AI-powered solutions that address specific business challenges.
Skill Requirements
Becoming a proficient Business Analyst demands a unique blend of technical prowess and soft skills. To thrive in this role, you’ll need to master a diverse skill set that encompasses both the analytical and interpersonal realms.
Let’s delve into the essential skills that define a successful Business Analyst, exploring both the core competencies and additional proficiencies that will set you apart.
Core Competencies and Technical Skills
- Data analysis and modeling: Uncover hidden patterns and trends in data to inform decision-making.
- Business process modeling and optimization: Analyze and improve business processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- Requirements elicitation and documentation: Gather, analyze, and document stakeholder requirements to ensure alignment.
- Project management and stakeholder management: Plan, execute, and manage projects while effectively engaging stakeholders.
- Data visualization and reporting: Present data insights in clear and compelling ways to drive informed decisions.
Soft Skills
- Communication (written and verbal): Convey complex ideas effectively both verbally and in writing.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking: Analyze problems, develop solutions, and make sound judgments.
- Stakeholder management and relationship-building: Build strong relationships with stakeholders to gain buy-in and support.
- Adaptability and flexibility: Embrace change, adjust to new situations, and learn new skills.
- Attention to detail and accuracy: Ensure accuracy and precision in all aspects of work.
Additional Skills
- Industry knowledge and experience: Understand the specific industry and domain you work in.
- Agile methodologies and tools: Familiarity with Agile frameworks and tools for efficient project delivery.
- Cloud computing and data management: Expertise in cloud platforms and data management techniques.
- Business intelligence and analytics: Leverage BI tools and techniques to derive insights from data.
- SQL and Python programming: Proficiency in SQL for data analysis and Python for automation.
Assessment of Skills
To assess the skills of Business Analysts, various methods are employed:
| Skill | Assessment Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Data analysis | Case study | Evaluates problem-solving and analytical abilities |
| Business process modeling | Skill test | Assesses proficiency in process modeling techniques |
| Communication | Interview | Examines verbal and written communication skills |
| Stakeholder management | Role-playing | Tests ability to interact effectively with stakeholders |
| Cloud computing | Certification | Verifies knowledge and expertise in cloud platforms |
Skill Development
To enhance your skills as a Business Analyst, consider these professional development opportunities:
- Workshops: Attend workshops on specific topics like data analysis or stakeholder management.
- Certifications: Obtain certifications in relevant areas like Business Analysis or Project Management.
- Online courses: Take online courses from reputable platforms to gain new skills or refresh existing ones.
Future Skills
As technology evolves, so do the skills required for Business Analysts. Emerging trends and technologies will shape the future of Business Analysis:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Proficiency in AI and ML techniques for data analysis and automation.
- Data Science: Expertise in data science concepts and tools to extract valuable insights from data.
- Agile at Scale: Mastery of Agile methodologies and frameworks for large-scale projects.
Best Practices

The efficiency and effectiveness of business analysts can be greatly enhanced by adhering to industry best practices. By implementing these proven methodologies and frameworks, analysts can ensure the delivery of high-quality solutions that meet the needs of stakeholders.
As a Business Analyst, navigating the challenges and seizing the opportunities in the field can be an exhilarating journey. Delving into Advanced Business Analysis empowers us with cutting-edge techniques and methodologies, enhancing our ability to analyze complex business problems, identify untapped opportunities, and drive meaningful change.
By embracing these advancements, we not only expand our professional capabilities but also position ourselves as indispensable assets in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Best Practices for Business Analysts
Here are some key best practices for business analysts:
- Use a structured methodology: This ensures a consistent and repeatable approach to business analysis, leading to improved efficiency and accuracy.
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Involving stakeholders throughout the analysis process increases buy-in and reduces the risk of misunderstandings.
- Document requirements thoroughly: Creating a clear and concise record of the requirements facilitates communication and reduces errors.
- Use visual modeling techniques: Visualizing and communicating complex requirements enhances understanding and reduces ambiguity.
- Test requirements thoroughly: Verifying that the requirements are complete, consistent, and testable minimizes the risk of defects in the final product.
“The key to successful business analysis is to understand the business problem and to develop a solution that meets the needs of the stakeholders.” – Business Analyst Institute
As a business analyst, navigating the challenges and seizing the opportunities of the profession requires a deep understanding of requirements discovery. By mastering the techniques and methodologies outlined in Requirements Discovery for Business Analyst , analysts can effectively elicit, analyze, and document business requirements, bridging the gap between stakeholders’ needs and the development of innovative solutions that drive business success.
Selecting the Right Methodology or Framework
The choice of methodology or framework depends on the specific needs of the project. Some popular options include:
- Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN)
- Unified Modeling Language (UML)
- Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK)
- International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA) Business Analysis Standards
By carefully considering the project requirements and selecting the most appropriate methodology or framework, business analysts can optimize their efficiency and effectiveness.
As a business analyst, you’ll face challenges and uncover opportunities that shape the future of organizations. To navigate these complexities, it’s crucial to master the fundamentals of business analysis. The Business Analysis Fundamentals – ECBA, CCBA, CBAP certification provides a comprehensive roadmap to equip you with the knowledge and skills to analyze business needs, design solutions, and drive positive change.
Embracing these certifications will empower you to excel as a business analyst, enabling you to identify opportunities and solve problems that drive business success.
Career Progression Paths for Business Analysts

Business Analysts play a crucial role in bridging the gap between business and technology, ensuring that projects meet the needs of both sides. As they gain experience and expertise, they can advance their careers in various directions, taking on specialized roles or moving into management positions.
The career progression path for Business Analysts typically involves several stages, each requiring specific skills and experience. Let’s explore the potential career paths and the skills and experience needed for each stage.
Entry-Level Business Analyst
Entry-level Business Analysts are typically responsible for gathering and analyzing requirements, creating documentation, and supporting project teams. They may also assist with testing and implementation.
- Skills: Strong analytical skills, communication skills, understanding of business processes, proficiency in business analysis tools
- Experience: 0-3 years of experience in business analysis or a related field
Mid-Level Business Analyst
Mid-level Business Analysts have gained more experience and are responsible for more complex projects. They may lead teams of junior analysts, participate in project planning, and develop solutions to business problems.
- Skills: Advanced analytical skills, strong stakeholder management skills, expertise in specific business domains, experience in agile methodologies
- Experience: 3-7 years of experience in business analysis
Senior Business Analyst
Senior Business Analysts are highly experienced professionals who provide strategic guidance to organizations. They may specialize in a particular area of business analysis, such as data analytics or process improvement.
- Skills: Exceptional analytical and problem-solving skills, deep understanding of business strategy, experience in managing large-scale projects
- Experience: 7+ years of experience in business analysis
Specialized Roles for Business Analysts
In addition to the traditional career path, Business Analysts can also pursue specialized roles that leverage their skills and experience in specific areas.
- Business Systems Analyst: Focuses on analyzing and improving business systems and processes
- Data Analyst: Uses data analysis techniques to extract insights and inform decision-making
- Process Analyst: Specializes in analyzing and optimizing business processes
- UX Analyst: Focuses on improving the user experience of software and applications
Factors Influencing Career Progression
Several factors can influence the career progression of Business Analysts, including:
- Industry: The industry in which a Business Analyst works can impact their career opportunities and advancement speed
- Company Size: Larger companies often provide more opportunities for career growth and specialization
- Individual Performance: Strong performance and a commitment to professional development can accelerate career progression
Case Studies

Real-world case studies provide tangible evidence of the value and impact of Business Analysts in diverse industries. These stories showcase how Business Analysts have successfully solved complex problems and driven positive business outcomes.
By examining these case studies, we gain valuable insights into the role of Business Analysts in:
- Identifying and analyzing business needs
- Developing and implementing solutions
- Evaluating the effectiveness of those solutions
Retail Industry
A leading retail company faced challenges in optimizing its inventory management system. The Business Analyst team conducted a thorough analysis of the existing system and identified inefficiencies in demand forecasting, resulting in overstocking and stockouts. They implemented a new demand forecasting model and streamlined the inventory replenishment process, leading to a significant reduction in inventory costs and improved customer satisfaction.
Healthcare Industry
A healthcare provider sought to improve the efficiency of its patient scheduling process. The Business Analyst team analyzed the current system and identified bottlenecks in appointment scheduling and patient flow. They designed and implemented a new scheduling system that automated the appointment scheduling process, reduced patient wait times, and improved the overall patient experience.
Financial Services Industry
A financial institution aimed to enhance its risk management capabilities. The Business Analyst team worked closely with the risk management team to identify and analyze potential risks. They developed and implemented a comprehensive risk management framework that included risk identification, assessment, and mitigation strategies, resulting in improved risk management practices and reduced operational risks.
The life of a Business Analyst is not just about analyzing business requirements and coming up with solutions. It’s also about understanding the user’s perspective and ensuring that the final product meets their needs. One crucial step in this process is User Acceptance Test (UAT).
UAT allows users to test the system and provide feedback, helping Business Analysts identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments. By incorporating UAT into the development process, Business Analysts can increase the likelihood of delivering a successful product that meets both business and user requirements.
Educational Programs for Business Analysts
Business analysts play a crucial role in the success of any organization. They bridge the gap between business stakeholders and IT teams, ensuring that technology solutions align with business goals. To become a successful business analyst, a strong educational foundation is essential.
There are several types of educational programs available for aspiring business analysts, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
Undergraduate Degrees, Problem & Opportunities of Business Analyst
- Typically four years in length
- Provide a broad foundation in business and technology
- May include specializations in business analysis or related fields
Graduate Degrees
- Typically one to two years in length
- Offer a more specialized education in business analysis
- May require a bachelor’s degree in a related field
Bootcamps
- Intensive programs typically lasting several weeks or months
- Focus on practical skills and hands-on experience
- May not provide a comprehensive education in business analysis
Online Courses
- Flexible and self-paced learning options
- Can provide a good foundation in business analysis
- May lack the hands-on experience and networking opportunities of in-person programs
Summary
The Problem & Opportunities of Business Analysts is a dynamic and evolving field, presenting both challenges and opportunities for these professionals. By embracing the latest trends and technologies, developing a strong foundation in core skills and competencies, and adhering to ethical principles, Business Analysts can unlock immense value for their organizations. As we navigate the complexities of the digital age, the role of Business Analysts will continue to grow in importance, shaping the future of business and technology.
Popular Questions
What are the key challenges faced by Business Analysts?
Business Analysts often face challenges in gathering and interpreting business requirements, managing stakeholder expectations, and keeping up with the pace of technological change.
What are the essential skills for a successful Business Analyst?
Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities, effective communication and stakeholder management skills, and proficiency in data analysis and modeling techniques are crucial for Business Analysts.
How can Business Analysts stay ahead of the curve in the digital age?
Business Analysts must continuously learn and adapt to emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, data visualization, and cloud computing, to remain relevant and valuable.

