The Overview of IT Business Analyst delves into the fascinating world of bridging technology and business objectives, where professionals play a pivotal role in aligning technology investments with organizational strategies. This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth understanding of the responsibilities, skills, methodologies, and impact of IT Business Analysts in today’s digital landscape.
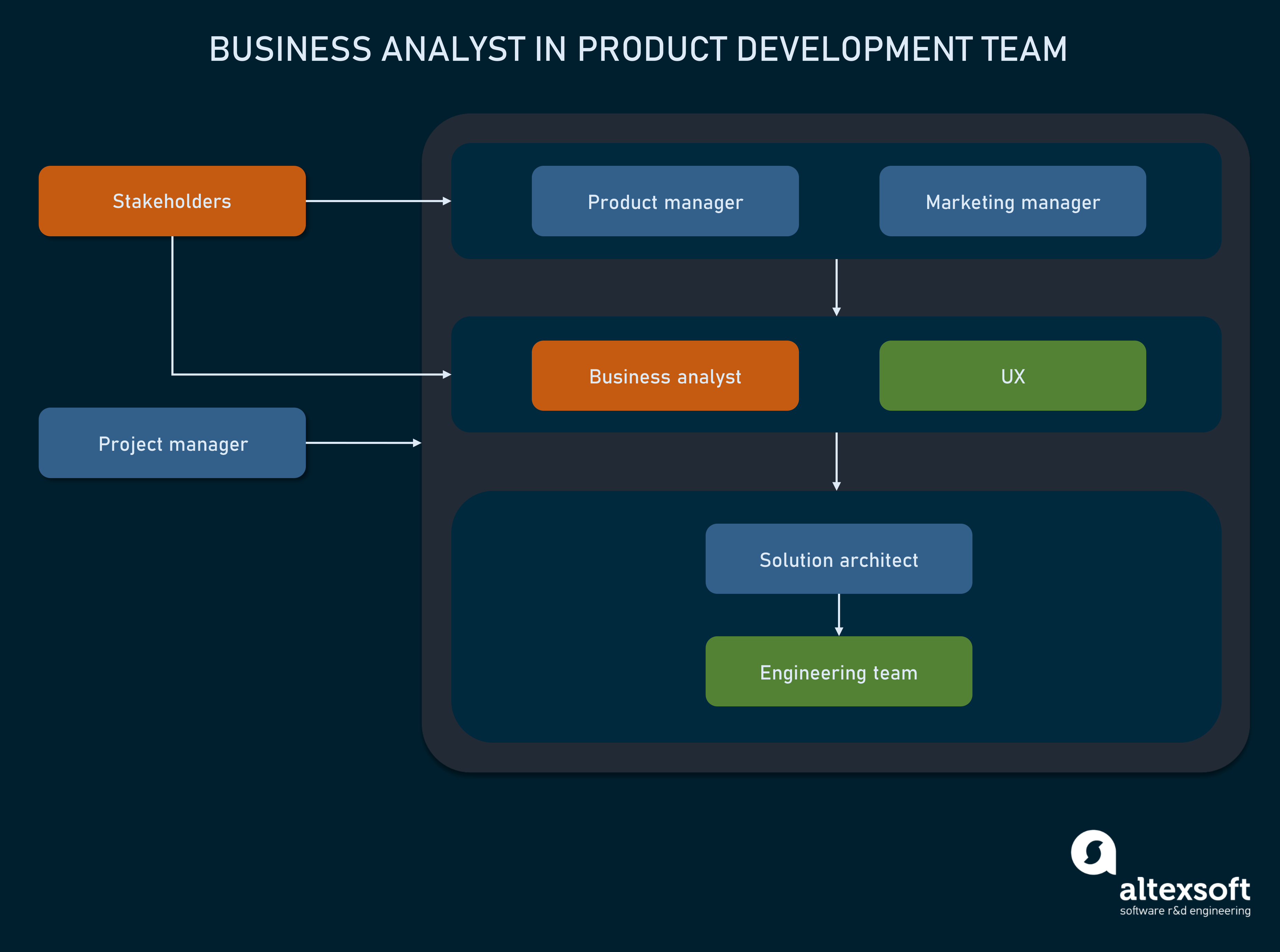
IT Business Analysts serve as the bridge between business stakeholders and technical teams, translating business requirements into technical solutions. They play a crucial role in ensuring that technology investments align with business goals, leading to improved efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Overview of the Role
An IT Business Analyst (BA) is a professional who acts as a bridge between the business and IT teams within an organization. They are responsible for understanding the business requirements and translating them into technical specifications that can be implemented by IT.
IT BAs play a crucial role in ensuring that IT projects are aligned with the business’s strategic goals and objectives. They work closely with stakeholders from both the business and IT sides to gather requirements, analyze data, and develop solutions that meet the needs of the organization.
Responsibilities of an IT Business Analyst
The responsibilities of an IT BA typically include:
- Gathering and analyzing business requirements
- Developing functional specifications and technical documentation
- Working with IT teams to implement and test solutions
- Providing training and support to end users
- Monitoring and evaluating IT projects
Skills and Qualifications Required for an IT Business Analyst
To be successful as an IT BA, individuals typically need the following skills and qualifications:
- A strong understanding of business processes and IT systems
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Analytical and problem-solving skills
- A bachelor’s degree in business, computer science, or a related field
- Experience in business analysis or a related field
Importance of IT Business Analysis
IT Business Analysis plays a crucial role in aligning technology with business objectives, ensuring that technology investments are informed and aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
IT business analysts play a crucial role in bridging the gap between business and technology. Their expertise extends beyond technical knowledge, encompassing a deep understanding of business processes, user needs, and industry trends. In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, IT business analysts are particularly valuable for their ability to translate business requirements into actionable IT solutions.
Just as Student Loan News provides comprehensive coverage on the latest developments in student loan financing, IT business analysts ensure that organizations remain competitive and responsive to changing market demands.
By understanding the business context, IT Business Analysts help bridge the gap between technology and business, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about technology investments that drive business value.
Aligning Technology with Business Objectives
- IT Business Analysts analyze business requirements and translate them into technical specifications, ensuring that technology solutions meet the specific needs of the organization.
- They assess the impact of technology on business processes and identify areas for improvement, helping organizations leverage technology to drive efficiency and innovation.
- By aligning technology with business objectives, IT Business Analysts help organizations maximize the value of their technology investments and achieve their strategic goals.
Making Informed Technology Investment Decisions
- IT Business Analysts conduct cost-benefit analysis and evaluate the potential risks and benefits of technology investments, providing organizations with a clear understanding of the return on investment.
- They assess the feasibility of technology solutions and identify potential challenges, ensuring that organizations make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the costs, benefits, and risks involved.
- By providing data-driven insights and analysis, IT Business Analysts help organizations prioritize technology investments and allocate resources effectively.
Business Analysis Process

Business analysis is a critical step in any IT project. It helps to ensure that the project is aligned with the business’s needs and that it will deliver the desired results. The business analysis process typically involves the following steps:
Requirements Gathering
The first step in business analysis is to gather requirements from the stakeholders. This can be done through interviews, workshops, and document reviews. It is important to involve all stakeholders in the requirements gathering process to ensure that all of their needs are met.
Requirements Analysis
Once the requirements have been gathered, they need to be analyzed to identify the underlying business needs. This can be done using a variety of techniques, such as use case analysis, data flow diagrams, and decision trees.
Solution Design
The next step is to design a solution that will meet the business needs. This can involve creating new systems, modifying existing systems, or implementing new processes. The solution design should be based on the requirements analysis and should take into account the constraints of the business.
Implementation
Once the solution has been designed, it needs to be implemented. This can involve developing new software, modifying existing software, or implementing new processes. It is important to have a plan in place for implementing the solution and to communicate this plan to all stakeholders.
Evaluation
The final step in the business analysis process is to evaluate the solution. This can be done by measuring the solution against the business requirements. It is important to evaluate the solution regularly to ensure that it is meeting the business needs and that it is delivering the desired results.
The business analysis process is a critical step in any IT project. It helps to ensure that the project is aligned with the business’s needs and that it will deliver the desired results.
| Step | Methodology | Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Requirements Gathering | Interviews, workshops, document reviews | Use case analysis, data flow diagrams, decision trees |
| Requirements Analysis | Use case analysis, data flow diagrams, decision trees | Interviews, workshops, document reviews |
| Solution Design | Use case analysis, data flow diagrams, decision trees | Interviews, workshops, document reviews |
| Implementation | Developing new software, modifying existing software, implementing new processes | Interviews, workshops, document reviews |
| Evaluation | Measuring the solution against the business requirements | Interviews, workshops, document reviews |
The following flowchart illustrates the flow of the business analysis process:
[Flowchart of Business Analysis Process]
Solution Design and Development

IT Business Analysts (BAs) play a crucial role in designing and developing IT solutions that meet business needs. They work closely with technical teams to translate business requirements into technical specifications and ensure that the developed solutions align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Responsibilities of IT BAs in Solution Design and Development
IT BAs have various responsibilities in the solution design and development process, including:
* Gathering and analyzing business requirements
* Developing functional specifications and technical documentation
* Creating wireframes and mockups to visualize the solution
* Collaborating with technical teams to implement the solution
* Testing and validating the solution
* Managing change requests and ensuring solution maintenance
Collaboration with Technical Teams
IT BAs collaborate closely with technical teams throughout the solution design and development process. They use tools such as Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams, wireframes, and mockups to communicate their ideas and requirements effectively. By working together, IT BAs and technical teams ensure that the developed solutions are both technically feasible and meet business needs.
Examples of Successful IT Solution Design and Development
Numerous examples showcase the successful design and development of IT solutions by IT BAs. For instance, in the healthcare industry, IT BAs have played a vital role in developing electronic health records systems that streamline patient care and improve efficiency. In the financial sector, IT BAs have helped create online banking platforms that provide secure and convenient access to financial services.
Challenges in Solution Design and Development
IT BAs may face various challenges in designing and developing IT solutions, including:
* Changing business requirements
* Limited technical resources
* Integration with legacy systems
* Data security and privacy concerns
To overcome these challenges, IT BAs must possess strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills. They should also stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies in IT solution design and development.
Staying Up-to-Date on Latest Trends and Technologies
IT BAs can stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies in IT solution design and development through various means, such as:
* Attending industry conferences and workshops
* Reading industry publications and whitepapers
* Participating in online forums and discussion groups
* Pursuing certifications and training programs
By staying informed about the latest advancements, IT BAs can ensure that the solutions they design and develop are innovative and meet the evolving needs of businesses.
Key Responsibilities of IT BAs in Solution Design and Development
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Gather and analyze business requirements | Identify and document the needs of the business stakeholders |
| Develop functional specifications and technical documentation | Create detailed specifications that Artikel the solution’s functionality and technical requirements |
| Create wireframes and mockups | Visualize the solution’s design and layout |
| Collaborate with technical teams | Work closely with developers, testers, and other technical professionals to implement the solution |
| Test and validate the solution | Ensure that the solution meets the business requirements and is free of defects |
| Manage change requests | Handle requests for changes to the solution’s design or functionality |
| Ensure solution maintenance | Monitor the solution’s performance and make necessary updates and enhancements |
“As an IT BA, I played a pivotal role in designing and developing a customer relationship management (CRM) system for a large retail organization. By working closely with business stakeholders and technical teams, we created a solution that streamlined customer interactions, improved sales efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction.” – Emily Carter, IT Business Analyst
Business Process Modeling
Business process modeling is a fundamental aspect of IT business analysis. It involves creating visual representations of business processes to document, analyze, and improve them.
There are various types of business process models, each serving specific purposes. Some common types include:
- Flowcharts: Represent the logical flow of a process using symbols and arrows.
- Value stream maps: Focus on identifying and eliminating waste in processes.
- Swimlane diagrams: Illustrate the roles and responsibilities involved in a process.
- Event-driven process chains: Model processes based on events and their triggers.
Business process models provide numerous benefits. They help:
- Visualize and document processes for better understanding.
- Identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks for improvement.
- Communicate processes effectively across stakeholders.
- Support decision-making and process optimization.
Challenges of Business Process Modeling
While valuable, business process modeling faces challenges:
- Data availability: Gathering accurate and complete data can be difficult.
- Complexity: Modeling complex processes can be challenging.
- Stakeholder involvement: Ensuring input and collaboration from all relevant stakeholders is crucial.
- Change management: Updating models to reflect process changes can be time-consuming.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, collaboration, and the use of appropriate tools.
IT Business Analysts play a critical role in aligning IT systems with business objectives, bridging the gap between technology and business needs. While their expertise is in high demand, recent developments such as the Student Loan Pause have highlighted the importance of understanding broader economic and social factors that can impact IT project outcomes.
By staying abreast of such external influences, IT Business Analysts can better anticipate and mitigate potential risks and ensure the successful delivery of IT solutions.
Role of IT in Business Process Modeling
IT plays a significant role in business process modeling:
- Data analysis: IT tools can help analyze process data to identify inefficiencies.
- Modeling software: IT provides software for creating and managing process models.
- Process automation: IT can automate processes based on models, improving efficiency.
IT tools enhance the accuracy, consistency, and efficiency of business process modeling.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Business Process Model
- Define the scope and objectives: Determine the purpose and boundaries of the model.
- Gather data: Collect information about the process from stakeholders and existing documentation.
- Create a draft model: Use a modeling tool or software to create an initial representation of the process.
- Validate the model: Review the model with stakeholders to ensure its accuracy and completeness.
- Finalize and document the model: Update the model based on feedback and document it for future reference.
Effective business process modeling requires a systematic approach, stakeholder involvement, and the use of appropriate IT tools.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Data analysis plays a crucial role in IT Business Analysis. IT Business Analysts leverage data to gain insights into business operations, identify inefficiencies, and formulate recommendations for improvement.
By analyzing data from various sources, such as transaction logs, customer surveys, and market research reports, IT Business Analysts can uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that inform decision-making. They use statistical techniques, data visualization tools, and machine learning algorithms to extract meaningful insights from raw data.
Data-Driven Recommendations
IT Business Analysts use data analysis to make informed recommendations that drive business outcomes. They identify areas for optimization, prioritize initiatives based on their potential impact, and develop solutions that address specific business challenges.
For instance, by analyzing sales data, an IT Business Analyst might identify a decline in sales in a particular region. They would then investigate the underlying causes, such as changes in customer preferences or increased competition, and recommend strategies to address the issue.
Support for Decision-Making
Data analysis also provides valuable support for decision-making within organizations. IT Business Analysts use data to quantify the potential impact of different options, assess risks and opportunities, and evaluate the effectiveness of implemented solutions.
IT Business Analysts play a crucial role in bridging the gap between business needs and technology solutions. They analyze business processes, identify inefficiencies, and recommend improvements that leverage technology. One notable example is Nelnet Student Loan , a leading provider of student loan servicing solutions.
Nelnet’s IT Business Analysts have implemented innovative solutions that streamline loan processing, improve customer experience, and reduce operating costs, demonstrating the transformative impact of IT Business Analysts in the financial sector.
By providing data-driven insights, IT Business Analysts empower stakeholders to make informed decisions that are aligned with business goals and objectives.
Communication and Presentation Skills for IT Business Analysts: Overview Of IT Business Analyst

Effective communication and presentation skills are crucial for IT Business Analysts (BAs) to persuade and influence stakeholders. These skills enable BAs to clearly convey complex technical concepts, gain buy-in for their recommendations, and drive successful project outcomes.
One way BAs can use communication skills to persuade stakeholders is by tailoring their message to the audience. By understanding the stakeholders’ interests, perspectives, and knowledge level, BAs can adapt their language, tone, and delivery to resonate with them. For example, when presenting to a technical audience, BAs can use technical jargon and detailed explanations, while when presenting to business stakeholders, they can focus on the business value and impact of the proposed solution.
Presentation skills are equally important for BAs to influence stakeholders. By using visuals, storytelling, and active listening, BAs can create engaging and persuasive presentations that capture the audience’s attention and leave a lasting impression. Visuals, such as charts, graphs, and diagrams, can help BAs illustrate complex concepts and make their presentations more visually appealing. Storytelling can be used to connect with the audience on an emotional level and make the presentation more memorable.
Active listening is essential for effective communication. By paying attention to what stakeholders are saying, both verbally and nonverbally, BAs can better understand their needs and concerns. This allows them to tailor their responses and build rapport with stakeholders, which is crucial for gaining their trust and support.
Empathy is another important aspect of effective communication. By putting themselves in the shoes of stakeholders, BAs can better understand their perspectives and motivations. This helps them to communicate in a way that is respectful and understanding, even when dealing with difficult stakeholders.
Key Communication and Presentation Skills for IT Business Analysts
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Tailoring Message | Adapting language, tone, and delivery to resonate with different audiences |
| Visual Communication | Using charts, graphs, and diagrams to illustrate complex concepts |
| Storytelling | Connecting with the audience on an emotional level through storytelling |
| Active Listening | Paying attention to what stakeholders are saying, both verbally and nonverbally |
| Empathy | Understanding the perspectives and motivations of stakeholders |
Tips for Improving Communication and Presentation Skills
- Practice active listening by paying attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues.
- Develop empathy by trying to understand the perspectives and motivations of others.
- Use visuals to make presentations more engaging and visually appealing.
- Incorporate storytelling into presentations to connect with the audience on an emotional level.
- Tailor your message to the audience by understanding their interests and knowledge level.
- Seek feedback on your communication and presentation skills to identify areas for improvement.
“Communication and presentation skills are essential for IT Business Analysts to effectively engage with stakeholders, build consensus, and drive successful project outcomes.” – [Industry Expert Name]
Industry Trends and Best Practices
The IT Business Analysis field is constantly evolving, with new trends and best practices emerging all the time. These trends are driven by the changing needs of businesses and the rapid pace of technological innovation.
Some of the most important trends in IT Business Analysis include the adoption of agile methodologies, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. Agile methodologies are designed to help teams deliver software faster and more efficiently, while data analytics can help businesses make better decisions by providing them with insights into their data. Artificial intelligence is also playing an increasingly important role in IT Business Analysis, as it can be used to automate tasks and improve decision-making.
IT Business Analysts are responsible for bridging the gap between business and technology. They help organizations understand their business needs and translate them into technical requirements. In the context of Student Loan Repayment , IT Business Analysts can play a crucial role in developing systems that streamline the repayment process and improve the overall experience for borrowers.
By understanding the challenges faced by both borrowers and lenders, IT Business Analysts can design solutions that meet the needs of all stakeholders.
In addition to these trends, there are also a number of best practices that can help IT Business Analysts succeed. These best practices include using requirements gathering tools, stakeholder engagement techniques, and risk management frameworks.
Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies are a set of software development practices that emphasize iterative development, team collaboration, and customer feedback. Agile methodologies have become increasingly popular in recent years, as they can help teams deliver software faster and more efficiently.
There are a number of different agile methodologies, but some of the most popular include Scrum, Kanban, and Lean. Each of these methodologies has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, but they all share a common goal of helping teams deliver software faster and more efficiently.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is the process of collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to extract meaningful insights. Data analytics can help businesses make better decisions by providing them with insights into their data.
There are a number of different data analytics tools and techniques available, and the best approach will vary depending on the specific needs of the business. However, some of the most common data analytics techniques include:
- Descriptive analytics: This type of analytics provides a summary of the data, such as the average, median, and mode.
- Diagnostic analytics: This type of analytics helps to identify the root causes of problems.
- Predictive analytics: This type of analytics uses historical data to predict future trends.
- Prescriptive analytics: This type of analytics provides recommendations on how to improve performance.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. AI is playing an increasingly important role in IT Business Analysis, as it can be used to automate tasks and improve decision-making.
There are a number of different AI techniques that can be used in IT Business Analysis, including:
- Machine learning: This technique allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural language processing: This technique allows computers to understand and generate human language.
- Computer vision: This technique allows computers to see and interpret images.
Best Practices
In addition to the trends discussed above, there are also a number of best practices that can help IT Business Analysts succeed. These best practices include:
- Using requirements gathering tools: These tools can help IT Business Analysts to gather and manage requirements from stakeholders.
- Stakeholder engagement techniques: These techniques can help IT Business Analysts to build relationships with stakeholders and get them involved in the project.
- Risk management frameworks: These frameworks can help IT Business Analysts to identify and mitigate risks.
By following these best practices, IT Business Analysts can increase their chances of success.
Conclusion
The IT Business Analysis field is constantly evolving, and it is important for IT Business Analysts to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices. By doing so, they can increase their chances of success and help their organizations to achieve their goals.
| Trend/Best Practice | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Agile methodologies | Faster software delivery, improved team collaboration, increased customer satisfaction | Can be difficult to implement, requires a change in mindset |
| Data analytics | Better decision-making, improved customer insights, increased operational efficiency | Can be complex and time-consuming, requires skilled data analysts |
| Artificial intelligence | Automated tasks, improved decision-making, increased efficiency | Can be expensive to implement, requires specialized skills |
| Requirements gathering tools | Improved requirements gathering, reduced errors, increased stakeholder involvement | Can be expensive, requires training |
| Stakeholder engagement techniques | Increased stakeholder buy-in, improved project outcomes, reduced risk | Can be time-consuming, requires strong interpersonal skills |
| Risk management frameworks | Reduced risk, improved project outcomes, increased stakeholder confidence | Can be complex and time-consuming, requires specialized knowledge |
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
The career path for IT Business Analysts offers various growth opportunities. With experience and expertise, IT Business Analysts can advance to senior roles with higher responsibilities and leadership positions.
Growth opportunities include:
Promotions, Overview of IT Business Analyst
- Senior IT Business Analyst: Manage larger and more complex projects, lead teams, and provide guidance to junior analysts.
- IT Business Analysis Manager: Oversee IT business analysis activities, manage resources, and ensure project success.
- Chief Business Analyst: Hold a senior leadership role, providing strategic direction and guidance on business analysis practices.
Potential Earnings
IT Business Analysts can earn competitive salaries based on their experience, skills, and industry. According to Salary.com, the average salary for IT Business Analysts in the United States is around $90,000 per year. Senior IT Business Analysts can earn up to $130,000 per year, while Chief Business Analysts can earn over $150,000 per year.
Case Studies and Examples
IT Business Analysis plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of IT projects. Here are some real-world case studies that illustrate the impact of IT Business Analysis:
Case Study 1: Business Process Optimization in a Healthcare System
A large healthcare system faced challenges with inefficient patient flow, resulting in long wait times and patient dissatisfaction. An IT Business Analyst conducted a thorough analysis of the existing processes, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Based on the analysis, the analyst proposed a new process design that optimized patient flow and reduced wait times by 30%.
Case Study 2: Data-Driven Decision Making in a Retail Company
A retail company wanted to improve its sales performance by understanding customer behavior. An IT Business Analyst analyzed customer data, identifying trends and patterns. The analysis revealed that certain product categories had higher sales potential, leading the company to adjust its marketing strategy. As a result, the company increased sales by 15%.
Key Factors for Success
The success of these IT Business Analysis projects can be attributed to several key factors:
- Strong collaboration between IT Business Analysts and business stakeholders
- Thorough understanding of business requirements and goals
- Use of appropriate analysis techniques and tools
- Effective communication and presentation skills
Challenges and Strategies
IT Business Analysis projects often face challenges, including:
- Changing business requirements
- Lack of stakeholder involvement
- Limited access to data
Strategies for overcoming these challenges include:
- Regular communication and stakeholder engagement
- Agile development methodologies
- Data governance and management practices
Evaluation Framework
To evaluate the effectiveness of IT Business Analysis initiatives, a framework can be used that includes metrics such as:
- Time to market
- Project cost
- Customer satisfaction
- Return on investment
By measuring these metrics, organizations can assess the value and impact of IT Business Analysis.
Table of Key Responsibilities
IT Business Analysts play a crucial role in bridging the gap between business needs and technical solutions. Their key responsibilities encompass a wide range of activities, including:
Elicitation and Documentation of Business Requirements
- Conducting interviews and workshops with stakeholders to gather and analyze business requirements.
- Documenting requirements using various techniques such as use cases, user stories, and business process models.
- Validating requirements with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Solution Design and Development
- Collaborating with technical teams to design and develop IT solutions that meet business requirements.
- Creating prototypes and mockups to demonstrate the functionality of proposed solutions.
- Testing and evaluating solutions to ensure they meet performance and usability criteria.
Business Process Modeling
- Analyzing and documenting existing business processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Designing and recommending new business processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- Collaborating with stakeholders to implement and monitor process changes.
Data Analysis and Reporting
- Collecting and analyzing data to understand business performance and identify trends.
- Creating reports and dashboards to communicate insights and recommendations to stakeholders.
- Using data analytics techniques to optimize business processes and decision-making.
List of Common Business Analysis Techniques

Business analysis techniques are tools and methodologies used by IT Business Analysts to gather, analyze, and interpret business requirements. These techniques help analysts understand the current state of a business, identify areas for improvement, and design and implement solutions that meet the needs of the organization.
There are many different business analysis techniques available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common techniques include:
| Technique Name | Description | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Interviews | One-on-one or group discussions with stakeholders to gather information about their needs and expectations. | Interviewing end-users to understand their pain points and desired outcomes. |
| Workshops | Facilitated sessions that bring together stakeholders to brainstorm ideas, develop solutions, and make decisions. | Conducting a workshop with business stakeholders to define the scope of a new project. |
| Document Analysis | Reviewing existing documents, such as process maps, system specifications, and user manuals, to gather information about the current state of a business. | Analyzing business process documentation to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. |
| Observation | Watching people work and observing their interactions with systems and processes to gain insights into their needs and behaviors. | Observing how employees use a software system to identify areas where the system can be improved. |
| Prototyping | Creating a mock-up or prototype of a new system or process to test its functionality and usability. | Developing a prototype of a new website to get feedback from users before it is fully implemented. |
| Use Case Analysis | Identifying and documenting the different ways that a system or process can be used. | Creating use cases for a new customer relationship management (CRM) system to ensure it meets the needs of all users. |
| Data Analysis | Collecting and analyzing data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can inform decision-making. | Analyzing sales data to identify which products are selling well and which are not. |
| SWOT Analysis | Identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing a business. | Conducting a SWOT analysis to assess the competitive landscape and identify potential areas for growth. |
Epilogue

In conclusion, IT Business Analysts are indispensable partners in driving organizational success through technology. Their expertise in bridging the gap between business and technology enables organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, the role of IT Business Analysts will only become more critical, shaping the future of business and technology integration.
General Inquiries
What are the key responsibilities of an IT Business Analyst?
IT Business Analysts are responsible for gathering and analyzing business requirements, designing and developing IT solutions, and ensuring alignment between technology and business objectives.
What skills are required for an IT Business Analyst?
IT Business Analysts typically require strong analytical, communication, and problem-solving skills, as well as knowledge of business processes and technology.
How does IT Business Analysis benefit organizations?
IT Business Analysis helps organizations make informed decisions about technology investments, improve business processes, and align technology with business goals.

